Deep Sequencing in Microdissected Renal Tubules Identifies Nephron Segment-Specific Transcriptomes
- PMID: 25817355
- PMCID: PMC4625681
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2014111067
Deep Sequencing in Microdissected Renal Tubules Identifies Nephron Segment-Specific Transcriptomes
Abstract
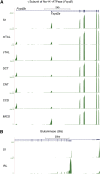
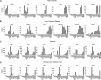
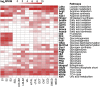
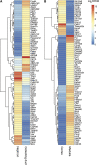
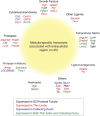
The function of each renal tubule segment depends on the genes expressed therein. High-throughput methods used for global profiling of gene expression in unique cell types have shown low sensitivity and high false positivity, thereby limiting the usefulness of these methods in transcriptomic research. However, deep sequencing of RNA species (RNA-seq) achieves highly sensitive and quantitative transcriptomic profiling by sequencing RNAs in a massive, parallel manner. Here, we used RNA-seq coupled with classic renal tubule microdissection to comprehensively profile gene expression in each of 14 renal tubule segments from the proximal tubule through the inner medullary collecting duct of rat kidneys. Polyadenylated mRNAs were captured by oligo-dT primers and processed into adapter-ligated cDNA libraries that were sequenced using an Illumina platform. Transcriptomes were identified to a median depth of 8261 genes in microdissected renal tubule samples (105 replicates in total) and glomeruli (5 replicates). Manual microdissection allowed a high degree of sample purity, which was evidenced by the observed distributions of well established cell-specific markers. The main product of this work is an extensive database of gene expression along the nephron provided as a publicly accessible webpage (https://helixweb.nih.gov/ESBL/Database/NephronRNAseq/index.html). The data also provide genome-wide maps of alternative exon usage and polyadenylation sites in the kidney. We illustrate the use of the data by profiling transcription factor expression along the renal tubule and mapping metabolic pathways.
Keywords: collecting ducts; nephron; transcription factors; transcriptional profiling.
Copyright © 2015 by the American Society of Nephrology.
Figures


Comment in
-
A Transcriptional Map of the Renal Tubule: Linking Structure to Function.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2015 Nov;26(11):2603-5. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2015030242. Epub 2015 Mar 27. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2015. PMID: 25817354 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Burg M, Grantham J, Abramow M, Orloff J: Preparation and study of fragments of single rabbit nephrons. Am J Physiol 210: 1293–1298, 1966 - PubMed
-
- Chabardès-Garonne D, Mejéan A, Aude JC, Cheval L, Di Stefano A, Gaillard MC, Imbert-Teboul M, Wittner M, Balian C, Anthouard V, Robert C, Ségurens B, Wincker P, Weissenbach J, Doucet A, Elalouf JM: A panoramic view of gene expression in the human kidney. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100: 13710–13715, 2003 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cheval L, Pierrat F, Dossat C, Genete M, Imbert-Teboul M, Duong Van Huyen JP, Poulain J, Wincker P, Weissenbach J, Piquemal D, Doucet A: Atlas of gene expression in the mouse kidney: New features of glomerular parietal cells. Physiol Genomics 43: 161–173, 2011 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

