APOBECs and virus restriction
- PMID: 25818029
- PMCID: PMC4424171
- DOI: 10.1016/j.virol.2015.03.012
APOBECs and virus restriction
Abstract
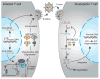
The APOBEC family of single-stranded DNA cytosine deaminases comprises a formidable arm of the vertebrate innate immune system. Pre-vertebrates express a single APOBEC, whereas some mammals produce as many as 11 enzymes. The APOBEC3 subfamily displays both copy number variation and polymorphisms, consistent with ongoing pathogenic pressures. These enzymes restrict the replication of many DNA-based parasites, such as exogenous viruses and endogenous transposable elements. APOBEC1 and activation-induced cytosine deaminase (AID) have specialized functions in RNA editing and antibody gene diversification, respectively, whereas APOBEC2 and APOBEC4 appear to have different functions. Nevertheless, the APOBEC family protects against both periodic viral zoonoses as well as exogenous and endogenous parasite replication. This review highlights viral pathogens that are restricted by APOBEC enzymes, but manage to escape through unique mechanisms. The sensitivity of viruses that lack counterdefense measures highlights the need to develop APOBEC-enabling small molecules as a new class of anti-viral drugs.
Keywords: APOBEC family; Cytosine deaminases; DNA viruses; Innate immunity; Retroviruses.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Abudu A, Takaori-Kondo A, Izumi T, Shirakawa K, Kobayashi M, Sasada A, Fukunaga K, Uchiyama T. Murine retrovirus escapes from murine APOBEC3 via two distinct novel mechanisms. Curr Biol. 2006;16:1565–1570. - PubMed
-
- Alce TM, Popik W. APOBEC3G is incorporated into virus-like particles by a direct interaction with HIV-1 Gag nucleocapsid protein. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:34083–34086. - PubMed
-
- Alexandrov LB, Nik-Zainal S, Wedge DC, Aparicio SA, Behjati S, Biankin AV, Bignell GR, Bolli N, Borg A, Borresen-Dale AL, Boyault S, Burkhardt B, Butler AP, Caldas C, Davies HR, Desmedt C, Eils R, Eyfjord JE, Foekens JA, Greaves M, Hosoda F, Hutter B, Ilicic T, Imbeaud S, Imielinsk M, Jager N, Jones DT, Jones D, Knappskog S, Kool M, Lakhani SR, Lopez-Otin C, Martin S, Munshi NC, Nakamura H, Northcott PA, Pajic M, Papaemmanuil E, Paradiso A, Pearson JV, Puente XS, Raine K, Ramakrishna M, Richardson AL, Richter J, Rosenstiel P, Schlesner M, Schumacher TN, Span PN, Teague JW, Totoki Y, Tutt AN, Valdes-Mas R, van Buuren MM, van ‘t Veer L, Vincent-Salomon A, Waddell N, Yates LR, Zucman-Rossi J, Futreal PA, McDermott U, Lichter P, Meyerson M, Grimmond SM, Siebert R, Campo E, Shibata T, Pfister SM, Campbell PJ, Stratton MR. Signatures of mutational processes in human cancer. Nature. 2013;500:415–421. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

