Enzalutamide: targeting the androgen signalling pathway in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer
- PMID: 25818596
- PMCID: PMC4744713
- DOI: 10.1111/bju.13123
Enzalutamide: targeting the androgen signalling pathway in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer
Abstract
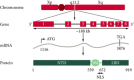
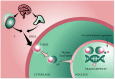
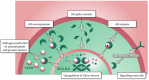
Significant progress has been made in the understanding of the underlying cancer biology of castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC) with the androgen receptor (AR) signalling pathway remaining implicated throughout the prostate cancer disease continuum. Reactivation of the AR signalling pathway is considered to be a key driver of CRPC progression and, as such, the AR is a logical target for therapy in CRPC. The objective of this review was to understand the importance of AR signalling in the treatment of patients with metastatic CRPC (mCRPC) and to discuss the clinical benefits associated with inhibition of the AR signalling pathway. A search was conducted to identify articles relating to the role of AR signalling in CRPC and therapies that inhibit the AR signalling pathway. Current understanding of prostate cancer has identified the AR signalling pathway as a logical target for the treatment of CRPC. Available therapies that inhibit the AR signalling pathway include AR blockers, androgen biosynthesis inhibitors, and AR signalling inhibitors. Enzalutamide, the first approved AR signalling inhibitor, has a novel mode of action targeting AR signalling at three key stages. The direct mode of action of enzalutamide has been shown to translate into clinical responses in patients with mCRPC. In conclusion, the targeting of the AR signalling pathway in patients with mCRPC results in numerous clinical benefits. As the number of treatment options increase, more trials evaluating the sequencing and combination of treatments are required. This review highlights the continued importance of targeting a key driver in the progression of CRPC, AR signalling, and the clinical benefits associated with inhibition of the AR signalling pathway in the treatment of patients with CRPC.
Keywords: androgen receptor signalling; castration-resistant; enzalutamide; mechanism of action; metastatic; prostate cancer.
© 2015 The Authors BJU International published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of BJU International.
Figures

References
-
- Gelmann EP. Molecular biology of the androgen receptor. J Clin Oncol 2002; 20: 3001–15 - PubMed
-
- Quigley CA, De Bellis A, Marschke KB, el‐Awady MK, Wilson EM, French FS. Androgen receptor defects: historical, clinical, and molecular perspectives. Endocr Rev 1995; 16: 271–321 - PubMed
-
- Heinlein CA, Chang C. Androgen receptor in prostate cancer. Endocr Rev 2004; 25: 276–308 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

