A MarR Family Transcriptional Regulator, DptR3, Activates Daptomycin Biosynthesis and Morphological Differentiation in Streptomyces roseosporus
- PMID: 25819953
- PMCID: PMC4421045
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.00057-15
A MarR Family Transcriptional Regulator, DptR3, Activates Daptomycin Biosynthesis and Morphological Differentiation in Streptomyces roseosporus
Abstract
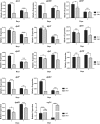
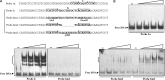
Daptomycin produced by Streptomyces roseosporus is an important lipopeptide antibiotic used to treat human infections caused by Gram-positive pathogenic bacteria, including drug-resistant strains. The genetic basis for regulatory mechanisms of daptomycin production is poorly known. Here, we characterized the dptR3 gene, which encodes a MarR family transcriptional regulator located adjacent to the known daptomycin biosynthetic (dpt) genes. Deletion of dptR3 reduced daptomycin production significantly and delayed aerial mycelium formation and sporulation on solid media. Dissection of the mechanism underlying the function of DptR3 in daptomycin production revealed that it stimulates daptomycin production indirectly by altering the transcription of dpt structural genes. DptR3 directly activated the transcription of its own gene, dptR3, but repressed the transcription of the adjacent, divergent gene orf16 (which encodes a putative ABC transporter ATP-binding protein). A 66-nucleotide DptR3-binding site in the intergenic region of dptR3-orf16 was determined by DNase I footprinting, and the palindromic sequence TCATTGTTACCTATGCTCACAATGA (underlining indicates inverted repeats) in the protected region was found to be essential for DptR3 binding. orf16, the major target gene of DptR3, exerted a positive effect on daptomycin biosynthesis. Our findings indicate that DptR3 functions as a global regulator that positively controls daptomycin production and morphological development in S. roseosporus.
Copyright © 2015, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Pleiotropic regulation of daptomycin synthesis by DptR1, a LuxR family transcriptional regulator.World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2020 Oct 20;36(11):173. doi: 10.1007/s11274-019-2771-1. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2020. PMID: 33079235
-
BldD, a master developmental repressor, activates antibiotic production in two Streptomyces species.Mol Microbiol. 2020 Jan;113(1):123-142. doi: 10.1111/mmi.14405. Epub 2019 Oct 19. Mol Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 31628680
-
DptR2, a DeoR-type auto-regulator, is required for daptomycin production in Streptomyces roseosporus.Gene. 2014 Jul 10;544(2):208-15. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2014.04.044. Epub 2014 Apr 23. Gene. 2014. PMID: 24768321
-
Regulation mechanisms underlying the biosynthesis of daptomycin and related lipopeptides.J Cell Biochem. 2012 Mar;113(3):735-41. doi: 10.1002/jcb.23414. J Cell Biochem. 2012. PMID: 22020738 Review.
-
The Gene bldA, a regulator of morphological differentiation and antibiotic production in streptomyces.Arch Pharm (Weinheim). 2015 Jul;348(7):455-62. doi: 10.1002/ardp.201500073. Epub 2015 Apr 27. Arch Pharm (Weinheim). 2015. PMID: 25917027 Review.
Cited by
-
m4C DNA methylation regulates biosynthesis of daptomycin in Streptomyces roseosporus L30.Synth Syst Biotechnol. 2022 Jun 17;7(4):1013-1023. doi: 10.1016/j.synbio.2022.06.001. eCollection 2022 Dec. Synth Syst Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 35801092 Free PMC article.
-
PicR as a MarR Family Transcriptional Repressor Multiply Controls the Transcription of Picolinic Acid Degradation Gene Cluster pic in Alcaligenes faecalis JQ135.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2022 Jun 14;88(11):e0017222. doi: 10.1128/aem.00172-22. Epub 2022 May 23. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35604228 Free PMC article.
-
A rational multi-target combination strategy for synergistic improvement of non-ribosomal peptide production.Nat Commun. 2025 Feb 22;16(1):1883. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-57073-5. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 39987186 Free PMC article.
-
A previously unidentified sugar transporter for engineering of high-yield Streptomyces.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2024 Dec;108(1):72. doi: 10.1007/s00253-023-12964-9. Epub 2024 Jan 9. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 38194147
-
Metabolic engineering of Streptomyces roseosporus for increased production of clinically important antibiotic daptomycin.Microb Biotechnol. 2024 Nov;17(11):e70038. doi: 10.1111/1751-7915.70038. Microb Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 39487765 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Miao V, Coëffet-Legal MF, Brian P, Brost R, Penn J, Whiting A, Martin S, Ford R, Parr I, Bouchard M, Silva CJ, Wrigley SK, Baltz RH. 2005. Daptomycin biosynthesis in Streptomyces roseosporus: cloning and analysis of the gene cluster and revision of peptide stereochemistry. Microbiology 151:1507–1523. doi:10.1099/mic.0.27757-0. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

