The RpoE Stress Response Pathway Mediates Reduction of the Virulence of Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli by Zinc
- PMID: 25819956
- PMCID: PMC4421060
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.00507-15
The RpoE Stress Response Pathway Mediates Reduction of the Virulence of Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli by Zinc
Abstract
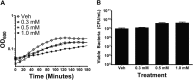
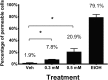
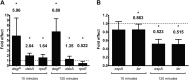
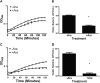
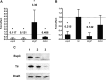
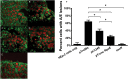
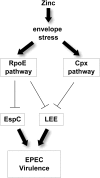
Zinc supplements are an effective clinical treatment for infantile diarrheal disease caused by enteric pathogens. Previous studies demonstrated that zinc acts on enteropathogenic Escherichia coli (EPEC) bacteria directly to suppress several virulence-related genes at a concentration that can be achieved by oral delivery of dietary zinc supplements. Our in vitro studies showed that a micromolar concentration of zinc induced the envelope stress response and suppressed virulence in EPEC, providing a possible mechanistic explanation for zinc's therapeutic action. In this report, we investigated the molecular and physiological changes in EPEC induced by zinc. We found that micromolar concentrations of zinc reduced the bacterial growth rate without affecting viability. We observed increased membrane permeability caused by zinc. Zinc upregulated the RpoE-dependent envelope stress response pathway and suppressed EPEC virulence gene expression. RpoE alone was sufficient to inhibit virulence factor expression and to attenuate attaching and effacing lesion formation on human host cells. By mutational analysis we demonstrate that the DNA-binding motif of RpoE is necessary for suppression of the LEE1, but not the LEE4, operon. Predictably, inhibition of the RpoE-mediated envelope stress response in combination with micromolar concentrations of zinc reduced EPEC viability. In conclusion, zinc induces the RpoE and stress response pathways in EPEC, and the alternate sigma factor RpoE downregulates EPEC LEE and non-LEE virulence genes by multiple mechanisms.
Copyright © 2015, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Shankar AH, Prasad AS. 1998. Zinc and immune function: the biological basis of altered resistance to infection. Am J Clin Nutr 68:447S–463S. - PubMed
-
- Lanata CF, Fischer-Walker CL, Olascoaga AC, Torres CX, Aryee MJ, Black RE, Child Health Epidemiology Reference Group of the World Health Organization and UNICEF. 2013. Global causes of diarrheal disease mortality in children <5 years of age: a systematic review. PLoS One 8:e72788. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0072788. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

