Nonsense-mediated RNA decay--a switch and dial for regulating gene expression
- PMID: 25820233
- PMCID: PMC4454373
- DOI: 10.1002/bies.201500007
Nonsense-mediated RNA decay--a switch and dial for regulating gene expression
Abstract
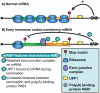
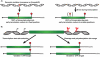
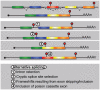
Nonsense-mediated RNA decay (NMD) represents an established quality control checkpoint for gene expression that protects cells from consequences of gene mutations and errors during RNA biogenesis that lead to premature termination during translation. Characterization of NMD-sensitive transcriptomes has revealed, however, that NMD targets not only aberrant transcripts but also a broad array of mRNA isoforms expressed from many endogenous genes. NMD is thus emerging as a master regulator that drives both fine and coarse adjustments in steady-state RNA levels in the cell. Importantly, while NMD activity is subject to autoregulation as a means to maintain homeostasis, modulation of the pathway by external cues provides a means to reprogram gene expression and drive important biological processes. Finally, the unanticipated observation that transcripts predicted to lack protein-coding capacity are also sensitive to this translation-dependent surveillance mechanism implicates NMD in regulating RNA function in new and diverse ways.
Keywords: gene regulation; noncoding RNA; nonsense-mediated RNA decay; quality control; translation termination.
© 2015 WILEY Periodicals, Inc.
Figures
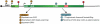



References
-
- Bhuvanagiri M, Schlitter AM, Hentze MW, Kulozik AE. NMD: RNA biology meets human genetic medicine. Biochem J. 2010;430:365–77. - PubMed
-
- Pulak R, Anderson P. MRNA surveillance by the Caenorhabditis elegans smg genes. Genes Dev. 1993;7:1885–97. - PubMed
-
- Behm-Ansmant I, Kashima I, Rehwinkel J, Sauliere J, et al. mRNA quality control: an ancient machinery recognizes and degrades mRNAs with nonsense codons. FEBS Lett. 2007;581:2845–53. - PubMed
-
- Schweingruber C, Rufener SC, Zund D, Yamashita A, et al. Nonsense-mediated mRNA decay - mechanisms of substrate mRNA recognition and degradation in mammalian cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013;1829:612–23. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

