Uncovering pharmacological mechanisms of Wu-tou decoction acting on rheumatoid arthritis through systems approaches: drug-target prediction, network analysis and experimental validation
- PMID: 25820382
- PMCID: PMC4377576
- DOI: 10.1038/srep09463
Uncovering pharmacological mechanisms of Wu-tou decoction acting on rheumatoid arthritis through systems approaches: drug-target prediction, network analysis and experimental validation
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: Uncovering pharmacological mechanisms of Wu-tou decoction acting on rheumatoid arthritis through systems approaches: drug-target prediction, network analysis and experimental validation.Sci Rep. 2018 Oct 30;8(1):15924. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-34061-y. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30375403 Free PMC article.
Abstract
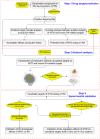
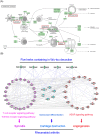
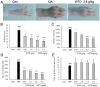
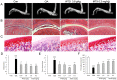
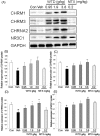
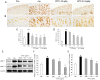
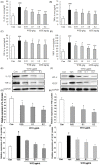
Wu-tou decoction (WTD) has been extensively used for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Due to lack of appropriate methods, pharmacological mechanisms of WTD acting on RA have not been fully elucidated. In this study, a list of putative targets for compositive compounds containing in WTD were predicted by drugCIPHER-CS. Then, the interaction network of the putative targets of WTD and known RA-related targets was constructed and hub nodes were identified. After constructing the interaction network of hubs, four topological features of each hub, including degree, node betweenness, closeness and k-coreness, were calculated and 79 major hubs were identified as candidate targets of WTD, which were implicated into the imbalance of the nervous, endocrine and immune (NEI) systems, leading to the main pathological changes during the RA progression. Further experimental validation also demonstrated the preventive effects of WTD on inflammation and joint destruction in collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) rats and its regulatory effects on candidate targets both in vitro and in vivo systems. In conclusion, we performed an integrative analysis to offer the convincing evidence that WTD may attenuate RA partially by restoring the balance of NEI system and subsequently reversing the pathological events during RA progression.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Pathway of PPAR-gamma coactivators in thermogenesis: a pivotal traditional Chinese medicine-associated target for individualized treatment of rheumatoid arthritis.Oncotarget. 2016 Mar 29;7(13):15885-900. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.7419. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 26895106 Free PMC article.
-
Guizhi-Shaoyao-Zhimu decoction attenuates rheumatoid arthritis partially by reversing inflammation-immune system imbalance.J Transl Med. 2016 Jun 8;14(1):165. doi: 10.1186/s12967-016-0921-x. J Transl Med. 2016. PMID: 27277474 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring and characterizing a novel combination of paeoniflorin and talatizidine for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis.Pharmacol Res. 2020 Mar;153:104658. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2020.104658. Epub 2020 Jan 27. Pharmacol Res. 2020. PMID: 32001347
-
Wutou decoction: A latest review on molecular mechanisms, clinical studies, quality control, pharmacokinetic studies, pharmacological effects, toxicity, and target prediction.J Ethnopharmacol. 2025 Feb 11;341:119307. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2024.119307. Epub 2024 Dec 30. J Ethnopharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39743182 Review.
-
The Effectiveness and Safety of Wu Tou Decoction on Rheumatoid Arthritis-A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Healthcare (Basel). 2024 Aug 31;12(17):1739. doi: 10.3390/healthcare12171739. Healthcare (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39273763 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Based on network pharmacology and molecular docking to explore the protective effect of Epimedii Folium extract on cisplatin-induced intestinal injury in mice.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Oct 12;13:1040504. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1040504. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36313368 Free PMC article.
-
Mesenchymal stem cells alleviate experimental rheumatoid arthritis through microRNA-regulated IκB expression.Sci Rep. 2016 Jun 29;6:28915. doi: 10.1038/srep28915. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27354158 Free PMC article.
-
A Network Pharmacology Approach to Uncover the Pharmacological Mechanism of XuanHuSuo Powder on Osteoarthritis.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2016;2016:3246946. doi: 10.1155/2016/3246946. Epub 2016 Mar 24. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2016. PMID: 27110264 Free PMC article.
-
The Chinese Medicine Wu-Tou Decoction Relieves Neuropathic Pain by Inhibiting Hippocampal Microglia Activation.Sci Rep. 2018 Aug 16;8(1):12292. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-30006-7. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30115941 Free PMC article.
-
A Network Pharmacology Approach to Explore the Pharmacological Mechanism of Xiaoyao Powder on Anovulatory Infertility.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2016;2016:2960372. doi: 10.1155/2016/2960372. Epub 2016 Dec 18. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2016. PMID: 28074099 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Böhler C. et al. Rheumatoid arthritis and falls: the influence of disease activity. Rheumatology (Oxford). 51, 2051–2057 (2012). - PubMed
-
- Nanke Y. et al. The effects of disease modifying anti-rheumatic drugs on osteoclastogenesis and bone destruction in rheumatoid arthritis. Nihon Rinsho Meneki Gakkai Kaishi. 34, 493–500 (2011). - PubMed
-
- Liu J. et al. The potential role of Chinese medicine in ameliorating extra-articular manifestations of rheumatoid arthritis. Chin J Integr Med. 17, 735–737 (2011). - PubMed
-
- Zhang S. Y. et al. Clinical observalion of modified Wu Tou Tang in the treatment of active rheumatoid arthriti. Chinese Journal of Traditional Medical Science and Technology. 17, 326–327 (2010)
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

