The double-histidine Cu²⁺-binding motif: a highly rigid, site-specific spin probe for electron spin resonance distance measurements
- PMID: 25821033
- PMCID: PMC4426033
- DOI: 10.1002/anie.201501968
The double-histidine Cu²⁺-binding motif: a highly rigid, site-specific spin probe for electron spin resonance distance measurements
Abstract
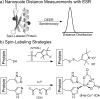
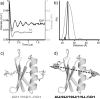
The development of ESR methods that measure long-range distance distributions has advanced biophysical research. However, the spin labels commonly employed are highly flexible, which leads to ambiguity in relating ESR measurements to protein-backbone structure. Herein we present the double-histidine (dHis) Cu(2+)-binding motif as a rigid spin probe for double electron-electron resonance (DEER) distance measurements. The spin label is assembled in situ from natural amino acid residues and a metal salt, requires no postexpression synthetic modification, and provides distance distributions that are dramatically narrower than those found with the commonly used protein spin label. Simple molecular modeling based on an X-ray crystal structure of an unlabeled protein led to a predicted most probable distance within 0.5 Å of the experimental value. Cu(2+) DEER with the dHis motif shows great promise for the resolution of precise, unambiguous distance constraints that relate directly to protein-backbone structure and flexibility.
Keywords: DEER; EPR spectroscopy; copper; proteins; spin labeling.
© 2015 WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Going the dHis-tance: Site-Directed Cu2+ Labeling of Proteins and Nucleic Acids.Acc Chem Res. 2021 Mar 16;54(6):1481-1491. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.0c00761. Epub 2021 Jan 21. Acc Chem Res. 2021. PMID: 33476119 Review.
-
On the Use of Q-Band Double Electron-Electron Resonance To Resolve the Relative Orientations of Two Double Histidine-Bound Cu2+ Ions in a Protein.J Phys Chem B. 2018 Nov 29;122(47):10669-10677. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcb.8b07727. Epub 2018 Nov 14. J Phys Chem B. 2018. PMID: 30372072
-
Differentiating between Label and Protein Conformers in Pulsed Dipolar EPR Spectroscopy with the dHis-Cu2+ (NTA) Motif.Chemistry. 2023 Dec 22;29(72):e202302541. doi: 10.1002/chem.202302541. Epub 2023 Nov 6. Chemistry. 2023. PMID: 37755452
-
Nucleotide-Independent Copper(II)-Based Distance Measurements in DNA by Pulsed ESR Spectroscopy.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2017 Feb 13;56(8):2115-2117. doi: 10.1002/anie.201611197. Epub 2017 Jan 16. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2017. PMID: 28090713
-
Protein Modeling with DEER Spectroscopy.Annu Rev Biophys. 2025 May;54(1):35-57. doi: 10.1146/annurev-biophys-030524-013431. Epub 2024 Dec 17. Annu Rev Biophys. 2025. PMID: 39689263 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Biophysical EPR Studies Applied to Membrane Proteins.J Phys Chem Biophys. 2015;5(6):188. doi: 10.4172/2161-0398.1000188. Epub 2015 Oct 15. J Phys Chem Biophys. 2015. PMID: 26855825 Free PMC article.
-
Nanomolar Pulse Dipolar EPR Spectroscopy in Proteins: CuII-CuII and Nitroxide-Nitroxide Cases.J Phys Chem B. 2021 May 27;125(20):5358-5364. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcb.1c03666. Epub 2021 May 17. J Phys Chem B. 2021. PMID: 33998795 Free PMC article.
-
Probing the Structure of Toxic Amyloid-β Oligomers with Electron Spin Resonance and Molecular Modeling.ACS Chem Neurosci. 2021 Apr 7;12(7):1150-1161. doi: 10.1021/acschemneuro.0c00714. Epub 2021 Mar 16. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 33724783 Free PMC article.
-
gem-Diethyl Pyrroline Nitroxide Spin Labels: Synthesis, EPR Characterization, Rotamer Libraries and Biocompatibility.ChemistryOpen. 2019 May 14;8(8):1057-1065. doi: 10.1002/open.201900119. eCollection 2019 Aug. ChemistryOpen. 2019. PMID: 31463171 Free PMC article.
-
Modeling of Cu(II)-based protein spin labels using rotamer libraries.Phys Chem Chem Phys. 2024 Feb 22;26(8):6806-6816. doi: 10.1039/d3cp05951k. Phys Chem Chem Phys. 2024. PMID: 38324256 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jeschke G. Prog. Nucl. Magn. Reson. Spectrosc. 2013;72:42–60. - PubMed
-
- Langen R, Oh KJ, Cascio D, Hubbell WL. Biochemistry. 2000;39:8396–8405. - PubMed
- Fleissner MR, Cascio D, Hubbell WL. Protein Sci. 2009;18:893–908. - PMC - PubMed
- Kroncke BM, Horanyi PS, Columbus L. Biochemistry. 2010;49:10045–10060. - PMC - PubMed
- Freed DM, Khan AK, Horanyi PS, Cafiso DS. Biochemistry. 2011;50:8792–8803. - PMC - PubMed
- Cunningham TF, McGoff MS, Sengupta I, Jaroniec CP, Horne WS, Saxena S. Biochemistry. 2012;51:6350–6359. - PubMed
-
- Fajer MI, Li H, Yang W, Fajer PG. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007;129:13840–13846. - PubMed
- Polyhach Y, Bordignon E, Jeschke G. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2011;13:2356–2366. - PubMed
- Hatmal MM, Li Y, Hegde BG, Hegde PB, Jao CC, Langen R, Haworth IS. Biopolymers. 2012;97:35–44. - PMC - PubMed
- Sarver J, Townsend J, Rajapakse G, Jen-Jacobson L, Saxena S. J. Phys. Chem. B. 2012;116:4024–4033. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

