Lipid and Protein Co-Regulation of PI3K Effectors Akt and Itk in Lymphocytes
- PMID: 25821452
- PMCID: PMC4358224
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2015.00117
Lipid and Protein Co-Regulation of PI3K Effectors Akt and Itk in Lymphocytes
Abstract
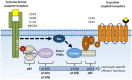
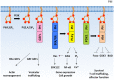
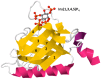
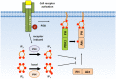
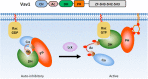
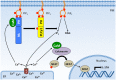
The phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI 3-kinase, PI3K) pathway transduces signals critical for lymphocyte function. PI3K generates the phospholipid PIP3 at the plasma membrane to recruit proteins that contain pleckstrin homology (PH) domains - a conserved domain found in hundreds of mammalian proteins. PH domain-PIP3 interactions allow for rapid signal propagation and confer a spatial component to these signals. The kinases Akt and Itk are key PI3K effectors that bind PIP3 via their PH domains and mediate vital processes - such as survival, activation, and differentiation - in lymphocytes. Here, we review the roles and regulation of PI3K signaling in lymphocytes with a specific emphasis on Akt and Itk. We also discuss these and other PH domain-containing proteins as they relate more broadly to immune cell function. Finally, we highlight the emerging view of PH domains as multifunctional protein domains that often bind both lipid and protein substrates to exert their effects.
Keywords: Akt signaling; Itk signaling; PI3K; lymphocyte activation; pleckstrin homology domain.
Figures
References
-
- Gadina M, Sudarshan C, Visconti R, Zhou YJ, Gu H, Neel BG, et al. The docking molecule gab2 is induced by lymphocyte activation and is involved in signaling by interleukin-2 and interleukin-15 but not other common gamma chain-using cytokines. J Biol Chem (2000) 275:26959–66.10.1074/jbc.M004021200 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

