Connectivity Study of the Neuromechanism of Acute Acupuncture Needling during fMRI in "Overweight" Subjects
- PMID: 25821486
- PMCID: PMC4363637
- DOI: 10.1155/2015/384389
Connectivity Study of the Neuromechanism of Acute Acupuncture Needling during fMRI in "Overweight" Subjects
Abstract
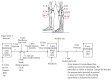
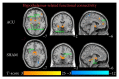
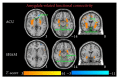
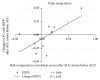
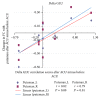
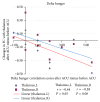
This functional connectivity study depicts how acupoints ST 36 and SP 9 and their sham acupoints acutely act on blood glucose (GLU), core body temperature (CBT), hunger, and sensations pertaining to needling (De-qi) via the limbic system and dopamine (DA) to affect various brain areas in fasting, adult, and "overweight" Chinese males using functional magnetic resonance imaging. Functional connectivity (FC) analysis utilized the amygdala (AMY) and hypothalamus (HYP) as regions of interest (ROIs) in the discrete cosine transform and seed correlation analysis methods. There was a significant difference in the spatial patterns of the distinct brain regions between groups. Correlation results showed that increased HYP-hippocampus FC after ACU was positively correlated with ACU-induced change in CBT; increased HYP-putamen-insula FC after ACU was positively correlated with ACU-induced change in GLU; and increased HYP-anterior cingulate cortex FC after ACU was positively correlated with ACU-induced change in HUNGER suggesting that increased DA modulation during ACU was probably associated with increased poststimulation limbic system and spinothalamic tract connectivity. Decreased HYP-thalamus FC after ACU was negatively correlated or anticorrelated with ACU-induced change in HUNGER suggesting that increased DA modulation during ACU was possibly associated with decreased poststimulation limbic system and spinothalamic tract connectivity. No correlation was found for min SHAM. This was an important study in addressing acute acupuncture effects and neural pathways involving physiology and appetite regulation in overweight individuals.
Figures


Similar articles
-
[Effect of acupuncture on brain functional connectivity strength in patients with primary dysmenorrhea].Zhongguo Zhen Jiu. 2022 Aug 12;42(8):863-70. doi: 10.13703/j.0255-2930.20210826-k0004. Zhongguo Zhen Jiu. 2022. PMID: 35938328 Chinese.
-
[Mind-regulating and spleen-strengthening needling technique improves abdominal hypersensitivity and emotion by enhancing functional connectivity between hippocampus and brain regions in diarrhea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome patients].Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2021 Apr 25;46(4):318-25. doi: 10.13702/j.1000-0607.200569. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2021. PMID: 33931998 Chinese.
-
[Effect of acupuncture on pain-emotion related brain regions in patients with cervical spondylosis of cervical type: a fMRI study].Zhongguo Zhen Jiu. 2021 Aug 12;41(8):906-12. doi: 10.13703/j.0255-2930.20201022-k0007. Zhongguo Zhen Jiu. 2021. PMID: 34369703 Chinese.
-
Effect of acupuncture at the acupoints for Yizhi Tiaoshen on the functional connectivity between the hippocampus and the brain in the patients with Alzheimer's disease.Zhongguo Zhen Jiu. 2023 Dec 12;43(12):1351-1357. doi: 10.13703/j.0255-2930.20230405-0002. Zhongguo Zhen Jiu. 2023. PMID: 38092531 Clinical Trial. Chinese, English.
-
Anterior cingulate cortex, insula and amygdala seed-based whole brain resting-state functional connectivity differentiates bipolar from unipolar depression.J Affect Disord. 2020 Sep 1;274:38-47. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2020.05.005. Epub 2020 May 22. J Affect Disord. 2020. PMID: 32469830
Cited by
-
Acute Effects of Different Electroacupuncture Point Combinations to Modulate the Gut-Brain Axis in the Minipig Model.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022 Oct 20;2022:4384693. doi: 10.1155/2022/4384693. eCollection 2022. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022. PMID: 36310617 Free PMC article.
-
Frequency of the Dopamine Receptor D3 (rs6280) vs. Opioid Receptor µ1 (rs1799971) Polymorphic Risk Alleles in Patients with Opioid Use Disorder: A Preponderance of Dopaminergic Mechanisms?Biomedicines. 2022 Apr 7;10(4):870. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10040870. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 35453620 Free PMC article.
-
Hypothesis paper: electroacupuncture targeting the gut-brain axis to modulate neurocognitive determinants of eating behavior-toward a proof of concept in the obese minipig model.Eat Weight Disord. 2021 Feb;26(1):61-74. doi: 10.1007/s40519-020-00864-0. Epub 2020 Feb 25. Eat Weight Disord. 2021. PMID: 32100220 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Blockade of the brachial plexus abolishes activation of specific brain regions by electroacupuncture at LI4: a functional MRI study.Acupunct Med. 2015 Dec;33(6):457-64. doi: 10.1136/acupmed-2015-010901. Epub 2015 Oct 13. Acupunct Med. 2015. PMID: 26464415 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Obesity Animal Models for Acupuncture and Related Therapy Research Studies.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021 Sep 30;2021:6663397. doi: 10.1155/2021/6663397. eCollection 2021. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021. PMID: 34630614 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

