Hepatoprotective Effect of Silymarin (Silybum marianum) on Hepatotoxicity Induced by Acetaminophen in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats
- PMID: 25821491
- PMCID: PMC4363982
- DOI: 10.1155/2015/538317
Hepatoprotective Effect of Silymarin (Silybum marianum) on Hepatotoxicity Induced by Acetaminophen in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats
Abstract
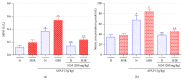
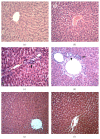
This study was aimed to investigate the effect of Silymarin (SLM) on the hypertension state and the liver function changes induced by acetaminophen (APAP) in spontaneously hypertensive rat (SHR). Animals normotensive (N) or hypertensive (SHR) were treated or not with APAP (3 g/kg, oral) or previously treated with SLM. Twelve hours after APAP administration, plasmatic levels of liver function markers: alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), glucose (GLU), gamma glutamyl transferase (γ-GT), and alkaline phosphatase (ALP) of all groups, were determined. Liver injury was assessed using histological studies. Samples of their livers were then used to determine the myeloperoxidase (MPO) activity and nitric oxide (NO) production and were also sectioned for histological analysis. No differences were observed for ALT, γ-GT, and GLU levels between SHR and normotensive rats groups. However, AST and ALP levels were increased in hypertensive animals. APAP treatment promoted an increase in ALT and AST in both SHR and N. However, only for SHR, γ-GT levels were increased. The inflammatory response evaluated by MPO activity and NO production showed that SHR was more susceptible to APAP effect, by increasing leucocyte infiltration. Silymarin treatment (Legalon) restored the hepatocyte functional and histopathological alterations induced by APAP in normotensive and hypertensive animals.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Hepatoprotective Effect of Citral on Acetaminophen-Induced Liver Toxicity in Mice.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2017;2017:1796209. doi: 10.1155/2017/1796209. Epub 2017 Jun 22. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2017. PMID: 28717379 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatoprotective effect of artichoke leaf extracts in comparison with silymarin on acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity in mice.J Immunoassay Immunochem. 2020;41(1):84-96. doi: 10.1080/15321819.2019.1692029. Epub 2019 Nov 18. J Immunoassay Immunochem. 2020. PMID: 31739724
-
Protective Effect of Cymbopogon citratus Essential Oil in Experimental Model of Acetaminophen-Induced Liver Injury.Am J Chin Med. 2017;45(3):515-532. doi: 10.1142/S0192415X17500318. Epub 2017 Mar 30. Am J Chin Med. 2017. PMID: 28359199
-
Moringa oleifera Lam prevents acetaminophen induced liver injury through restoration of glutathione level.Food Chem Toxicol. 2008 Aug;46(8):2611-5. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2008.04.018. Epub 2008 Apr 25. Food Chem Toxicol. 2008. PMID: 18514995
-
Are alterations needed in Silybum marianum (Silymarin) administration practices? A novel outlook and meta-analysis on randomized trials targeting liver injury.BMC Complement Med Ther. 2025 Apr 12;25(1):134. doi: 10.1186/s12906-025-04886-y. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2025. PMID: 40221681 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Hepatoprotective effect of β-myrcene pretreatment against acetaminophen-induced liver injury.Avicenna J Phytomed. 2022 Jul-Aug;12(4):388-400. doi: 10.22038/AJP.2022.19493. Avicenna J Phytomed. 2022. PMID: 35782770 Free PMC article.
-
Potential Curative Effects of Aqueous Extracts of Cissus quadrangularis (Vitaceae) and Jatropha gossypiifolia (Euphorbiaceae) on Acetaminophen-Induced Liver Injury in Mice.Curr Ther Res Clin Exp. 2023 Sep 30;99:100716. doi: 10.1016/j.curtheres.2023.100716. eCollection 2023. Curr Ther Res Clin Exp. 2023. PMID: 37869400 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatoprotective Effect of Citral on Acetaminophen-Induced Liver Toxicity in Mice.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2017;2017:1796209. doi: 10.1155/2017/1796209. Epub 2017 Jun 22. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2017. PMID: 28717379 Free PMC article.
-
In Vitro Antioxidant Activities and the Therapeutic Potential of Some Newly Synthesized Chalcones Against 4-Acetaminophenol Induced Hepatotoxicity in Rats.Dose Response. 2021 Mar 15;19(1):1559325821996955. doi: 10.1177/1559325821996955. eCollection 2021 Jan-Mar. Dose Response. 2021. PMID: 33795997 Free PMC article.
-
Medicinal herbs and their metabolites with biological potential to protect and combat liver toxicity and its disorders: A review.Heliyon. 2024 Feb 1;10(3):e25340. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e25340. eCollection 2024 Feb 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38356556 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Mambelli E. Arterial hypertension in dialysis: up to what point should it be corrected? It depends. GiornaleItaliano di Nefrologia. 2011;28(3):261–265. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

