The effect of electroacupuncture with different frequencies on muscle oxygenation in humans
- PMID: 25821493
- PMCID: PMC4363685
- DOI: 10.1155/2015/620785
The effect of electroacupuncture with different frequencies on muscle oxygenation in humans
Abstract
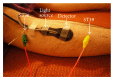
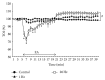
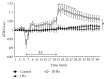
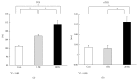
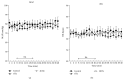
The aim of the present study was to investigate the effect of electroacupuncture (EA) with different frequencies on muscle oxygenation in humans. The subjects were 8 healthy male volunteers. Muscle oxygenation was measured using near-infrared spectroscopy (NIRS). Blood pressure (BP) and heart rate (HR) were monitored simultaneously. After baseline recording, EA was given for 15 min and recovery was measured for 20 minutes. The procedure of EA at 1 Hz, at 20 Hz, and at control followed in the same subjects. Tissue oxygenation index (TOI) decreased during EA at 20 Hz (P < 0.05) and increased during the recovery period. Normalized tissue hemoglobin index (nTHI) also decreased during EA at 20 Hz and increased during the recovery period (P < 0.05), whereas TOI and nTHI in the EA at 1 Hz did not change significantly throughout the experiment. The peak TOI and nTHI values at 20 Hz during the recovery period were higher than the values at 1 Hz and in the control (P < 0.05). BP and HR remained constant. These data suggest that the supply of oxygen to muscle decreased during EA at 20 Hz and increased after EA at 20 Hz, without any changes in HR and BP.
Figures
References
-
- Grassi B., Pogliaghi S., Rampichini S., et al. Muscle oxygenation and pulmonary gas exchange kinetics during cycling exercise on-transitions in humans. Journal of Applied Physiology. 2003;95(1):149–158. - PubMed
-
- Tew G. A., Ruddock A. D., Saxton J. M. Skin blood flow differentially affects near-infrared spectroscopy-derived measures of muscle oxygen saturation and blood volume at rest and during dynamic leg exercise. European Journal of Applied Physiology. 2010;110(5):1083–1089. doi: 10.1007/s00421-010-1596-2. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

