Enhancement of the acrolein-induced production of reactive oxygen species and lung injury by GADD34
- PMID: 25821552
- PMCID: PMC4364366
- DOI: 10.1155/2015/170309
Enhancement of the acrolein-induced production of reactive oxygen species and lung injury by GADD34
Abstract
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is characterized by lung destruction and inflammation. As a major compound of cigarette smoke, acrolein plays a critical role in the induction of respiratory diseases. GADD34 is known as a growth arrest and DNA damage-related gene, which can be overexpressed in adverse environmental conditions. Here we investigated the effects of GADD34 on acrolein-induced lung injury. The intranasal exposure of acrolein induced the expression of GADD34, developing the pulmonary damage with inflammation and increase of reactive oxygen species (ROS). Conversely, the integrality of pulmonary structure was preserved and the generation of ROS was reduced in GADD34-knockout mice. Acrolein-induced phosphorylation of eIF2α in GADD34-knockout epithelial cells by shRNA protected cell death by reducing misfolded protein-caused oxidative stress. These data indicate that GADD34 participates in the development of acrolein-induced lung injury.
Figures
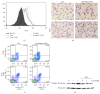

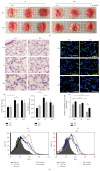
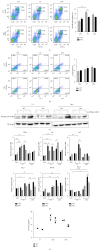
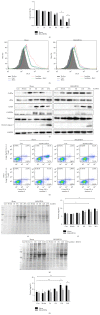
Similar articles
-
Idh2 Deficiency Exacerbates Acrolein-Induced Lung Injury through Mitochondrial Redox Environment Deterioration.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2017;2017:1595103. doi: 10.1155/2017/1595103. Epub 2017 Dec 31. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2017. PMID: 29456784 Free PMC article.
-
Acrolein induced both pulmonary inflammation and the death of lung epithelial cells.Toxicol Lett. 2014 Sep 2;229(2):384-92. doi: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2014.06.021. Epub 2014 Jul 5. Toxicol Lett. 2014. PMID: 24999835
-
GADD34 Facilitates Cell Death Resulting from Proteasome Inhibition.Anticancer Res. 2015 Oct;35(10):5317-24. Anticancer Res. 2015. PMID: 26408692
-
Acrolein effects in pulmonary cells: relevance to chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2012 Jul;1259:39-46. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2012.06531.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2012. PMID: 22758635 Review.
-
Proposed Mode of Action for Acrolein Respiratory Toxicity Associated with Inhaled Tobacco Smoke.Toxicol Sci. 2016 Jun;151(2):347-64. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfw051. Epub 2016 Mar 11. Toxicol Sci. 2016. PMID: 26969371 Review.
Cited by
-
Açai Berry Attenuates Cyclophosphamide-Induced Damage in Genitourinary Axis-Modulating Nrf-2/HO-1 Pathways.Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Nov 28;11(12):2355. doi: 10.3390/antiox11122355. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36552563 Free PMC article.
-
Response of DNA damage genes in acrolein-treated lung adenocarcinoma cells.Mol Cell Biochem. 2019 Jan;450(1-2):187-198. doi: 10.1007/s11010-018-3385-x. Epub 2018 Jul 2. Mol Cell Biochem. 2019. PMID: 29968166
-
Based on bioinformatics, SESN2 negatively regulates ferroptosis induced by ischemia reperfusion via the System Xc-/GPX4 pathway.Front Genet. 2025 Jan 29;15:1504114. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2024.1504114. eCollection 2024. Front Genet. 2025. PMID: 39944356 Free PMC article.
-
Multi-omics reveal neuroprotection of Acer truncatum Bunge Seed extract on hypoxic-ischemia encephalopathy rats under high-altitude.Commun Biol. 2023 Oct 2;6(1):1001. doi: 10.1038/s42003-023-05341-9. Commun Biol. 2023. PMID: 37783835 Free PMC article.
-
Preventive and therapeutic effects of Nasturtium officinale hydroalcoholic extract on cyclophosphamide-induced testicular toxicity in rats.Avicenna J Phytomed. 2025 May-Jun;15(3):1091-1101. doi: 10.22038/ajp.2025.25887. Avicenna J Phytomed. 2025. PMID: 40365180 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hogg J. C. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: an overview of pathology and pathogenesis. Novartis Foundation Symposium. 2001;234:4–19, 26. - PubMed
-
- Lacroix L., Feng G., Lotan R. Identification of genes expressed differentially in an in vitro human lung carcinogenesis model. Cancer Biology and Therapy. 2006;5(6):665–673. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

