Brain abscess after percutaneous therapy for trigeminal neuralgia
- PMID: 25821610
- PMCID: PMC4363676
- DOI: 10.1155/2015/162793
Brain abscess after percutaneous therapy for trigeminal neuralgia
Abstract
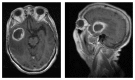
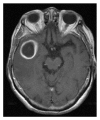
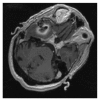
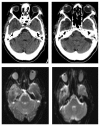
We report a case of brain abscess following the percutaneous treatment for trigeminal neuralgia. This procedure envisages the access with a needle into the middle cranial fossa through the oral cavity. Thus, in this case, the bacterial infection can be more likely ascribed to the possible contamination of the needle inside the oral cavity rather than to other frequent and more controllable causes of infection like an imperfect sterilization of surgical instruments or an inadequate antiseptic preparation of both operator's hands and patient's skin. The subsequent brain abscess was treated with antibiotic therapy (Vancomycin 2 gr a day and Meropenem 8 g a day for 22 days before the surgical procedure and 30 days after, until complete normalization of laboratory parameters, clinical parameters, and neurological symptoms) and surgical drainage, although the culture of the abscess capsule and the purulent material resulted sterile. In conclusion, the percutaneous therapy for trigeminal neuralgia can be objectively related to risks, even if performed by expert hands. Therefore, it is important that the patient should be advised regarding risks/benefits and/or septic complications of such procedures, even if they occur very seldom. An association of surgery and antibiotic therapy results as effective treatment for this pathologic condition.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Peritonsillar abscess: clinical aspects of microbiology, risk factors, and the association with parapharyngeal abscess.Dan Med J. 2017 Mar;64(3):B5333. Dan Med J. 2017. PMID: 28260599 Review.
-
CT-guided minimally invasive treatment for an extensive spinal epidural abscess: a case report and literature review.Eur Spine J. 2018 Jul;27(Suppl 3):380-385. doi: 10.1007/s00586-017-5307-0. Epub 2017 Sep 22. Eur Spine J. 2018. PMID: 28951964 Review.
-
Spinal epidural abscess successfully treated with percutaneous, computed tomography-guided, needle aspiration and parenteral antibiotic therapy: case report and review of the literature.Neurosurgery. 2002 Aug;51(2):509-12; discussion 512. Neurosurgery. 2002. PMID: 12182793 Review.
-
Persistent trigeminal neuralgia after removal of contralateral posterior cranial fossa tumor. Report of two cases.Surg Neurol. 1999 Jul;52(1):56-60; discussion 60-1. doi: 10.1016/s0090-3019(99)00050-6. Surg Neurol. 1999. PMID: 10390175
-
Ultrasound-Guided Pulsed Radiofrequency Application via the Pterygopalatine Fossa: A Practical Approach to Treat Refractory Trigeminal Neuralgia.Pain Physician. 2015 May-Jun;18(3):E411-5. Pain Physician. 2015. PMID: 26000688
Cited by
-
High-Resolution MRI Findings following Trigeminal Rhizotomy.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2016 Oct;37(10):1920-1924. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A4868. Epub 2016 Jun 30. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2016. PMID: 27365326 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources