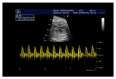
Drug resistant fetal arrhythmia in obstetric cholestasis
- PMID: 25821617
- PMCID: PMC4363709
- DOI: 10.1155/2015/890802
Drug resistant fetal arrhythmia in obstetric cholestasis
Abstract
Obstetric cholestasis (OC) is a pregnancy specific liver disease characterized by increased levels of bile acid (BA) and pruritus. Raised maternal BA levels could be associated with intrauterine death, fetal distress, and preterm labor and also alter the rate and rhythm of cardiomyocyte contraction and may cause fetal arrhythmic events. We report a case of drug resistant fetal supraventricular tachycardia and concomitant OC. Conclusion. If there are maternal OC and concomitant fetal arrhythmia, possibility of the resistance to antiarrhythmic treatment should be kept in mind.
Figures
References
-
- Villavicencio K. L. Fetal arrhythmias. In: Drose J. A., editor. Fetal Echocardiography. St. Louis, Mo, USA: Elsevier Saunders; 2010. pp. 306–320.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources