Transition zone prostate specific antigen density improves prostate cancer detection in Iranian men
- PMID: 25821749
- PMCID: PMC4360524
- DOI: 10.5812/numonthly.26752
Transition zone prostate specific antigen density improves prostate cancer detection in Iranian men
Abstract
Background: Prostate specific antigen (PSA) as a tumor marker has extensively changed the diagnosis of prostate cancer (PCa). With the advent of PSA, the majority of patients are diagnosed with nonpalpable early stage PCa. However, PSA lacks specificity and many patients undergo unnecessary biopsies due to an elevated serum PSA level.
Objectives: This study aimed to assess the sensitivity and specificity of transition zone PSA density (TZPSAD) in detection of PCa.
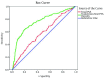
Patients and methods: This study was performed on 1712 men underwent trans-rectal ultrasound guided prostate biopsy in our institution between March 2008 and March 2013. A total of 1120 men with PSA < 20 ng/mL and normal digital rectal exam were selected for evaluation. Transition zone PSA density was calculated in all patients and the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve was used to analyze the accuracy of TZPSAD for the diagnosis of PCa.
Results: Among 1120 men who were eligible for enrolment, prostate cancer was detected in 265 patients. Mean serum PSA levels were 9.7 ± 4.3 ng/mL and 8.5 ± 3.7 ng/mL in patients with and without PCa, respectively (P < 0.001). Mean value for TZPSAD was 1.18 ± 1.19 ng/mL/mL in patients with PCa, whereas it was 0.55 ± 0.84 ng/mL in men without cancer (P < 0.001). Optimal cut-off value for TZPSAD was 0.32 ng/mL. At this cut-off value, the sensitivity and specificity values for TZPSAD were 85% and 45%, respectively. Applying the TZPSAD for PCa screening decreased 50% of unnecessary biopsies.
Conclusions: Using TZPSAD as an adjunct to PSA may improve the specificity of PSA in the diagnosis of PCa and decrease the number of unnecessary prostatic biopsies in Iranian men with serum PSA level < 20 ng/mL.
Keywords: Prostate-Specific Antigen; Prostatic Neoplasms; ROC Curve; Sensitivity and Specificity.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Zonal adjusted PSA density improves prostate cancer detection rates compared with PSA in Taiwanese males with PSA < 20 ng/ml.BMC Urol. 2020 Oct 7;20(1):151. doi: 10.1186/s12894-020-00717-z. BMC Urol. 2020. PMID: 33028274 Free PMC article.
-
Transition zone PSA density improves the prostate cancer detection rate both in PSA 4.0-10.0 and 10.1-20.0 ng/ml in Chinese men.Urol Oncol. 2013 Aug;31(6):744-8. doi: 10.1016/j.urolonc.2011.06.012. Epub 2011 Aug 24. Urol Oncol. 2013. PMID: 21868261
-
The value of percent free prostate specific antigen, prostate specific antigen density of the whole prostate and of the transition zone in Turkish men.Can J Urol. 2000 Oct;7(5):1104-9. Can J Urol. 2000. PMID: 11114873
-
Evaluation of prostate specific antigen density and transrectal ultrasonography-guided biopsies in 100 consecutive patients with a negative digital rectal examination and intermediate serum prostate specific antigen levels.Int J Urol. 1997 Jul;4(4):362-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1442-2042.1997.tb00209.x. Int J Urol. 1997. PMID: 9256325 Review.
-
Prospective evaluation of prostate specific antigen density and systematic biopsy for detecting prostate cancer in Japanese patients with normal rectal examinations and intermediate prostate specific antigen levels.J Urol. 1997 Sep;158(3 Pt 1):861-4. doi: 10.1097/00005392-199709000-00046. J Urol. 1997. PMID: 9258099 Review.
Cited by
-
Zonal adjusted PSA density improves prostate cancer detection rates compared with PSA in Taiwanese males with PSA < 20 ng/ml.BMC Urol. 2020 Oct 7;20(1):151. doi: 10.1186/s12894-020-00717-z. BMC Urol. 2020. PMID: 33028274 Free PMC article.
-
The roles of MRI-based prostate volume and associated zone-adjusted prostate-specific antigen concentrations in predicting prostate cancer and high-risk prostate cancer.PLoS One. 2019 Nov 19;14(11):e0218645. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0218645. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31743339 Free PMC article.
-
Peripheral zone volume ratio (PZ-ratio) is relevant with biopsy results and can increase the accuracy of current diagnostic modality.Oncotarget. 2017 May 23;8(21):34836-34843. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.16753. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28422738 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Oesterling JE. Prostate specific antigen: a critical assessment of the most useful tumor marker for adenocarcinoma of the prostate. J Urol. 1991;145(5):907–23. - PubMed
-
- Benson MC, Whang IS, Olsson CA, McMahon DJ, Cooner WH. The use of prostate specific antigen density to enhance the predictive value of intermediate levels of serum prostate specific antigen. J Urol. 1992;147(3 Pt 2):817–21. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous