Rap1 is indispensable for TRF2 function in etoposide-induced DNA damage response in gastric cancer cell line
- PMID: 25821946
- PMCID: PMC4491608
- DOI: 10.1038/oncsis.2015.1
Rap1 is indispensable for TRF2 function in etoposide-induced DNA damage response in gastric cancer cell line
Abstract
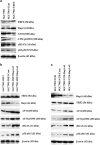
The telomeric protein TRF2, involving in telomeric and extratelomeric DNA damage response, has been previously reported to facilitate multidrug resistance (MDR) in gastric cancer cells by interfering ATM-dependent DNA damage response induced by anticancer drugs. Rap1 is the TRF2-interacting protein in the shelterin complex. Complex formation between Rap1 and TRF2 is essential for their function in telomere and end protection. Here we focus on the effects of Rap1 on TRF2 function in DNA damage response induced by anticancer drugs. Both Rap1 and TRF2 expression were upregulated in SGC7901 and its MDR variant SGC7901/VCR after etoposide treatment, which was more marked in SGC7901/VCR than in SGC7901. Rap1 silencing by siRNA in SGC7901/VCR partially reversed the etoposide resistance. And Rap1 silencing partially reversed the TRF2-mediated resistance to etoposide in SGC7901. Rap1 silencing did not affect the TRF2 upregulation induced by etoposide, but eliminated the inhibition effect of TRF2 on ATM expression and ATM phosphorylation at serine 1981 (ATM pS1981). Furthermore, phosphorylation of ATM targets, including γH2AX and serine 15 (S15) on p53, were increased in Rap1 silencing cells in response to etoposide. Thus, we confirm that Rap1, interacting with TRF2 in the shelterin complex, also has an important role in TRF2-mediated DNA damage response in gastric cancer cells treated by etoposide.
Figures


Similar articles
-
TRF2 promotes multidrug resistance in gastric cancer cells.Cancer Biol Ther. 2006 Aug;5(8):950-6. doi: 10.4161/cbt.5.8.2877. Epub 2006 Aug 2. Cancer Biol Ther. 2006. PMID: 16760674
-
Human Rap1 modulates TRF2 attraction to telomeric DNA.Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Mar 11;43(5):2691-700. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv097. Epub 2015 Feb 11. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015. PMID: 25675958 Free PMC article.
-
TRF2-Mediated Control of Telomere DNA Topology as a Mechanism for Chromosome-End Protection.Mol Cell. 2016 Jan 21;61(2):274-86. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2015.12.009. Epub 2016 Jan 7. Mol Cell. 2016. PMID: 26774283 Free PMC article.
-
DNA processing is not required for ATM-mediated telomere damage response after TRF2 deletion.Nat Cell Biol. 2005 Jul;7(7):712-8. doi: 10.1038/ncb1275. Epub 2005 Jun 19. Nat Cell Biol. 2005. PMID: 15968270
-
RAP1/TERF2IP-A Multifunctional Player in Cancer Development.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Nov 27;13(23):5970. doi: 10.3390/cancers13235970. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34885080 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Novel combination of tanshinone I and lenalidomide induces chemo-sensitivity in myeloma cells by modulating telomerase activity and expression of shelterin complex and its associated molecules.Mol Biol Rep. 2018 Dec;45(6):2429-2439. doi: 10.1007/s11033-018-4409-z. Epub 2018 Oct 11. Mol Biol Rep. 2018. PMID: 30311125
-
Identification of an immune-related gene-based signature to predict prognosis of patients with gastric cancer.World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2020 Aug 15;12(8):857-876. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v12.i8.857. World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32879664 Free PMC article.
-
Suppression of STN1 enhances the cytotoxicity of chemotherapeutic agents in cancer cells by elevating DNA damage.Oncol Lett. 2016 Aug;12(2):800-808. doi: 10.3892/ol.2016.4676. Epub 2016 Jun 2. Oncol Lett. 2016. PMID: 27446354 Free PMC article.
-
Telomerase and Telomeres in Endometrial Cancer.Front Oncol. 2019 May 17;9:344. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2019.00344. eCollection 2019. Front Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31157162 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CROssBAR: comprehensive resource of biomedical relations with knowledge graph representations.Nucleic Acids Res. 2021 Sep 20;49(16):e96. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkab543. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021. PMID: 34181736 Free PMC article.
References
-
- de Lange T. Shelterin: the protein complex that shapes and safeguards human telomeres. Genes Dev. 2005;19:2100–2110. - PubMed
-
- Wright WE, Shay JW. Telomere-binding factors and general DNA repair. Nat. Genet. 2005;37:116–118. - PubMed
-
- Huda N, Abe S, Gu L, Mendonca MS, Mohanty S, Gilley D. Recruitment of TRF2 to laser-induced DNA damage sites. Free Radic Biol Med. 2012;53:1192–1197. - PubMed
-
- Bradshaw PS, Stavropoulos DJ, Meyn MS. Human telomeric protein TRF2 associates with genomic double-strand breaks as an early response to DNA damage. Nat Genet. 2005;37:193–197. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

