Week 120 efficacy of tenofovir, lamivudine and lopinavir/r-based second-line antiretroviral therapy in treatment-experienced HIV patients
- PMID: 25821963
- PMCID: PMC4379083
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0120705
Week 120 efficacy of tenofovir, lamivudine and lopinavir/r-based second-line antiretroviral therapy in treatment-experienced HIV patients
Abstract
Background: Tenofovir (TDF) and ritonavir-boosted lopinavir (LPV/r) were not introduced to China as second-line medications until 2009. The efficacy and safety of TDF/3TC/LPV/r based second-line regimen have not been evaluated in Chinese HIV patients who failed first-line regimens.
Methods: This was a multicenter cohort study recruiting patients from Beijing, Shanghai, Guangdong, and Henan provinces between November 2008 and January 2010. Eighty HIV infected patients failing first-line regimens with serum creatinine lower than 1.5 times the upper limit of normal received TDF+ lamivudine (3TC)+ LPV/r were followed up for 120 weeks. CD4 cell count, viral load, and estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) were monitored at each visit.
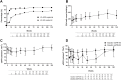
Results: At baseline, 31.2% and 48.8% of patients had moderate/high-level resistance to TDF and 3TC, respectively; while 2.5% of patients had only low-level resistance to LPV/r. During 120 weeks of follow-up, virological suppression rate reached over 70% (<40 copies/ml) and 90% (<400 copies/ml), and median CD4 cell count increased from 157 cells/μL at baseline to 307 cells/μL at week 120. Baseline drug-resistance mutations had no impact on the efficacy of second-line antiretroviral therapy. Median eGFR dropped from 104.7 ml/min/1.73m2 at baseline to 95.6 ml/min/1.73m2 at week 24 and then recovered after week 96.
Conclusion: This study for the first time demonstrated that TDF+ 3TC+ LPV/r was efficacious as second-line regimen with acceptable nephrotoxicity profiles in patients who failed zidovudine or stavudine based first-line regimens in China.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00872417.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Zhang F, Dou Z, Ma Y, Zhao Y, Liu Z, Bulterys M, et al. Five-year outcomes of the China National Free Antiretroviral Treatment Program. Ann Intern Med. 2009;151:241–251, w–252. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization. Antiretroviral therapy for HIV infection in adults and adolescents: recommendations for a public health approach, 2010 revision. 2010. - PubMed
-
- Cao Y, Han Y, Xie J, Cui Q, Zhang L, Li Y, et al. Impact of a tenofovir disoproxil fumarate plus ritonavir-boosted protease inhibitor-based regimen on renal function in HIV-infected individuals: a prospective, multicenter study. BMC Infect Dis. 2013;13:301 10.1186/1471-2334-13-301 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

