Dereplication of known nucleobase and nucleoside compounds in natural product extracts by capillary electrophoresis-high resolution mass spectrometry
- PMID: 25822081
- PMCID: PMC6272742
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules20045423
Dereplication of known nucleobase and nucleoside compounds in natural product extracts by capillary electrophoresis-high resolution mass spectrometry
Abstract
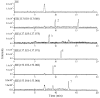
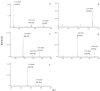
Nucleobase and nucleoside compounds exist widely in various organisms. An often occurring problem in the discovery of new bioactive compounds from natural products is reisolation of known nucleobase and nucleoside compounds. To resolve this problem, a capillary electrophoresis-high resolution mass spectrometry (CE-HR-MS) method providing both rapid separation and accurate mass full-scan MS data was developed for the first time to screen and dereplicate known nucleobase and nucleoside compounds in crude extracts of natural products. Instrumental parameters were optimized to obtain optimum conditions for CE separation and electrospray ionization-time-of-flight mass spectrometry (ESI-TOF/MS) detection. The proposed method was verified to be precise, reproducible, and sensitive. Using this method, known nucleobase and nucleoside compounds in different marine medicinal organisms including Syngnathus acus Linnaeus; Hippocampus japonicus Kaup and Anthopleura lanthogrammica Berkly were successfully observed and identified. This work demonstrates that CE-HR-MS combined with an accurate mass database may be used as a powerful tool for dereplicating known nucleobase and nucleoside compounds in different types of natural products. Rapid dereplication of known nucleobase and nucleoside compounds allows researchers to focus on other leads with greater potential to yield new substances.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
[Comparison of different buffer systems for separation of 15 nucleosides by capillary electrophoresis].Se Pu. 2011 Jun;29(6):481-7. doi: 10.3724/sp.j.1123.2011.00481. Se Pu. 2011. PMID: 22032157 Chinese.
-
Rapid screening and identification of the antioxidants in Hippocampus japonicus Kaup by HPLC-ESI-TOF/MS and on-line ABTS free radical scavenging assay.J Sep Sci. 2010 Mar;33(4-5):672-7. doi: 10.1002/jssc.200900544. J Sep Sci. 2010. PMID: 20127911
-
Separation of nucleobases, nucleosides, and nucleotides using two zwitterionic silica-based monolithic capillary columns coupled with tandem mass spectrometry.J Chromatogr A. 2014 Dec 19;1373:90-6. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2014.11.015. Epub 2014 Nov 14. J Chromatogr A. 2014. PMID: 25465366
-
Capillary electrophoresis-electrospray ionization-mass spectrometry interfaces: fundamental concepts and technical developments.J Chromatogr A. 2012 Dec 7;1267:17-31. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2012.07.019. Epub 2012 Jul 16. J Chromatogr A. 2012. PMID: 22846629 Review.
-
Screening bioactive compounds from natural product and its preparations using capillary electrophoresis.Electrophoresis. 2018 Jan;39(1):260-274. doi: 10.1002/elps.201700239. Epub 2017 Oct 4. Electrophoresis. 2018. PMID: 28891070 Review.
Cited by
-
Analysis of Three Compounds in Flos Farfarae by Capillary Electrophoresis with Large-Volume Sample Stacking.Int J Anal Chem. 2017;2017:3813879. doi: 10.1155/2017/3813879. Epub 2017 Sep 5. Int J Anal Chem. 2017. PMID: 29056967 Free PMC article.
-
Fast Simultaneous Determination of 13 Nucleosides and Nucleobases in Cordyceps sinensis by UHPLC-ESI-MS/MS.Molecules. 2015 Dec 4;20(12):21816-25. doi: 10.3390/molecules201219807. Molecules. 2015. PMID: 26690105 Free PMC article.
-
Cryosphere: a frozen home of microbes and a potential source for drug discovery.Arch Microbiol. 2024 Mar 28;206(4):196. doi: 10.1007/s00203-024-03899-4. Arch Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38546887 Review.
References
-
- Yang J., Liang Q., Wang M., Jeffries C., Smithson D., Tu Y., Boulos N., Jacob M.R., Shelat A.A., Wu Y.S., et al. UPLC-MS-ELSD-PDA as a powerful dereplication tool to facilitate compound identification from small-molecule natural product libraries. J. Nat. Prod. 2014;77:902–909. doi: 10.1021/np4009706. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Tchoumtchoua J., Njamen D., Mbanya J.C., Skaltsounis A.L., Halabalaki M. Structure-oriented UHPLC-LTQ orbitrap-based approach as a dereplication strategy for the identification of isoflavonoids from Amphimas pterocarpoides crude extract. J. Mass. Spectrom. 2013;48:561–575. doi: 10.1002/jms.3167. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

