Surgical interventions for treating distal tibial metaphyseal fractures in adults
- PMID: 25822346
- PMCID: PMC8924865
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD010261.pub2
Surgical interventions for treating distal tibial metaphyseal fractures in adults
Abstract
Background: The distal tibial metaphysis is located in the lower (distal) part of the tibia (shin bone). Fractures of this part of the tibia are most commonly due to a high energy injury in young men and to osteoporosis in older women. The optimal methods of surgical intervention for a distal tibial metaphyseal fracture remain uncertain.
Objectives: To assess the effects (benefits and harms) of surgical interventions for distal tibial metaphyseal fractures in adults. We planned to compare surgical versus non-surgical (conservative) treatment, and different methods of surgical intervention.
Search methods: We searched the Cochrane Bone, Joint and Muscle Trauma Group Specialised Register (9 December 2014), the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (2014, Issue 12), MEDLINE (1946 to November Week 3 2014), EMBASE (1980 to 2014 Week 48), the Airiti Library (1967 to 2014 Week 8), China Knowledge Resource Integrated Database (1915 to 2014 Week 8), ClinicalTrials.gov (February 2014) and reference lists of included studies.
Selection criteria: We included randomised and quasi-randomised controlled clinical studies comparing surgical versus non-surgical (conservative) treatment or different surgical interventions for treating distal tibial metaphyseal fractures in adults. Our primary outcomes were patient-reported function and the need for secondary or revision surgery or substantive physiotherapy because of adverse outcomes.
Data collection and analysis: Two authors independently selected studies, assessed the risk of bias in each study and extracted data. We resolved disagreement by discussion and, where necessary, in consultation with a third author. Where appropriate we pooled data using the fixed-effect model.
Main results: We included three randomised trials that evaluated intramedullary nailing versus plating in 213 participants, with useable data from 173 participants of whom 112 were male. The mean age of participants in individual studies ranged from 41 to 44 years. There were no trials comparing surgery with non-surgical treatment. The three included trials were at high risk of performance bias, with one trial also being at high risk of selection, detection and attrition bias. Overall, the quality of available evidence was rated as very low for all outcomes, meaning that we are very unsure about the estimates for all outcomes.The results of two large ongoing trials of nailing versus plating are likely to provide sufficient evidence to address this issue in a future update.
Authors' conclusions: Overall, there is either no or insufficient evidence to draw definitive conclusions on the use of surgery or the best surgical intervention for distal tibial metaphyseal fractures in adults. The available evidence, which is of very low quality, found no clinically important differences in function or pain, and did not confirm a difference in the need for re-operation or risk of complications between nailing and plating.The addition of evidence from two ongoing trials of nailing versus plating should inform this question in future updates. Further randomised trials are warranted on other issues, but should be preceded by research to identify priority questions.
Conflict of interest statement
Liang Tseng Kuo: none known Ching‐Chi Chi: none known Ching‐Hui Chuang: none known
Figures

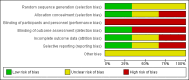











Update of
- doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010261
Similar articles
-
Interventions for treating fractures of the distal femur in adults.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Aug 13;2015(8):CD010606. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010606.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Oct 5;10:CD010606. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010606.pub3. PMID: 26270891 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Surgical interventions for treating acute fractures or non-union of the middle third of the clavicle.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 May 7;2015(5):CD007428. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007428.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. PMID: 25950424 Free PMC article.
-
Intramedullary nailing for tibial shaft fractures in adults.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Jan 18;1(1):CD008241. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008241.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012. PMID: 22258982 Free PMC article.
-
Surgical fixation methods for tibial plateau fractures.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Sep 15;2015(9):CD009679. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009679.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024 Aug 22;8:CD009679. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009679.pub3. PMID: 26370268 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Interventions for treating fractures of the patella in adults.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Feb 27;(2):CD009651. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009651.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Feb 24;2:CD009651. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009651.pub3. PMID: 25723760 Updated.
Cited by
-
May minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis be an alternative to intramedullary nailing in selected spiral oblique and spiral wedge tibial shaft fractures?Jt Dis Relat Surg. 2020;31(3):494-501. doi: 10.5606/ehc.2020.75052. Jt Dis Relat Surg. 2020. PMID: 32962581 Free PMC article.
-
Surgical Management of Distal Tibia Fracture: Towards An Outcome-based Treatment Algorithm.Malays Orthop J. 2020 Nov;14(3):57-65. doi: 10.5704/MOJ.2011.010. Malays Orthop J. 2020. PMID: 33403063 Free PMC article.
-
Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis for short oblique diaphyseal tibia fractures: does fracture site affect the outcomes?J Int Med Res. 2020 Oct;48(10):300060520965402. doi: 10.1177/0300060520965402. J Int Med Res. 2020. PMID: 33086906 Free PMC article.
-
A systematic review and meta-analysis of functional outcomes and complications following external fixation or open reduction internal fixation for distal intra-articular tibial fractures: an update.Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2019 May;29(4):907-917. doi: 10.1007/s00590-019-02368-9. Epub 2019 Feb 9. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2019. PMID: 30739163
-
An intuitive and simple technique for accurate insertion point selection and precise Poller (blocking) screw insertion.Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2020 Oct;140(10):1431-1435. doi: 10.1007/s00402-020-03398-3. Epub 2020 Mar 6. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2020. PMID: 32144503
References
References to studies included in this review
Guo 2010 {published data only}
-
- Guo JJ, Tang N, Yang HL, Tang TS. A prospective, randomised trial comparing closed intramedullary nailing with percutaneous plating in the treatment of distal metaphyseal fractures of the tibia [Erratum appears in Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery. British Volume 2010;92(12):1717]. Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery. British Volume 2010;92(7):984‐8. - PubMed
Im 2005 {published data only}
-
- Im GI, Tae SK. Distal metaphyseal fractures of tibia: a prospective randomized trial of closed reduction and intramedullary nail versus open reduction and plate and screws fixation. Journal of Trauma 2005;59(5):1219‐23. [PUBMED: 16385303] - PubMed
Mauffrey 2012 {published data only}
-
- Mauffrey C. Raw data enquiry [personal communication]. Email to: LT Kuo 20 May 2013.
-
- Mauffrey C, McGuinness K, Parsons N, Achten J, Costa ML. A randomised pilot trial of "locking plate" fixation versus intramedullary nailing for extra‐articular fractures of the distal tibia. Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery. British volume 2012;94(5):704‐8. - PubMed
-
- Mauffrey C, McGuinness K, Parsons N, Achten J, Costa ML. A randomised pilot trial of intramedullary nailing versus 'locking‐plate' fixation for extra‐articular fractures of the distal tibia (abstract). Injury 2011;42(10):974. - PubMed
-
- Mauffrey C, McGuinness KR, Parsons N, Achten J, Costa ML. A randomised pilot trial of intramedullary nailing versus 'locking‐plate' fixation for extra‐articular fractures of the distal tibia (abstract). American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Annual Meeting; 2012 Mar 7‐11; San Francisco (CA). 2012.
References to studies excluded from this review
Cheng 2011 {published data only}
Dai 2009 {published data only}
-
- Dai JP, Yan YQ, Yu YF, Zhou X. Curative effect comparison of two methods of treatment for distal tibial fractures [Chinese] [脛骨遠端骨折兩種治療方法的療效比較]. Zhongguo gu shang [China Journal of Orthopaedics and Traumatology] 2009;22(5):361‐3. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Hontzsch 2014 {published data only}
-
- Hoentzsch D. Trial to evaluate the effectiveness of angular stable locking system (ASLS) in patients with distal tibial fractures. clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT00875992 (accessed 19 March 2015).
-
- Hontzsch D, Schaser KD, Hofmann GO, Pohlemann T, Hem ES, Rothenbach E, et al. Evaluation of the effectiveness of the angular stable locking system in patients with distal tibial fractures treated with intramedullary nailing: a multicenter randomized controlled trial. Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery. American Volume 2014;96(22):1889‐97. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Li 2014 {published data only}
Liu 2014 {published data only}
-
- Liu CH, Wang ZC, Lu H, Yu SM, Mao YL, Zhou Q. Percutaneous locking plate versus traditional anatomical plate fixation for distal tibial fracture. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu 2014;18(17):2703‐8.
Ristiniemi 2011 {published data only}
-
- Ristiniemi J, Luukinen P, Ohtonen P. Surgical treatment of extra‐articular or simple intra‐articular distal tibial fractures: external fixation versus intramedullary nailing. Journal of Orthopaedic Trauma 2011;25(2):101‐5. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Shon 2012 {published data only}
-
- Shon OJ, Park CH. Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis of distal tibial fractures: a comparison of medial and lateral plating. Journal of Orthopaedic Science 2012;17(5):562‐6. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Sun 2014 {published data only}
-
- Sun LJ, Wu ZP, Guo XS, Chen H. Management of distal third tibial fractures: comparison of combined internal and external fixation with minimally invasive percutaneous plate osteosynthesis. International Orthopaedics 2014;38(11):2349‐55. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Vallier 2011 {published data only}
-
- Vallier HA, Cureton BA, Patterson BM. Randomized, prospective comparison of plate versus intramedullary nail fixation for distal tibia shaft fractures. Journal of Orthopaedic Trauma 2011;25(12):736‐41. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Vallier 2012 {published data only}
-
- Vallier HA, Cureton BA, Patterson BM. Factors influencing functional outcomes after distal tibia shaft fractures. Journal of Orthopaedic Trauma 2012;26:178‐83. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Yang 2006 {published data only}
-
- Yang SW, Tzeng HM, Chou YJ, Teng HP, Liu HH, Wong CY. Treatment of distal tibial metaphyseal fractures: plating versus shortened intramedullary nailing. Injury 2006;37(6):531‐5. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Zou 2012 {published data only}
-
- Zou J, Shi ZM, Zhang W, Zhang CQ. Open reduction and internal fixation better than percutaneous plate osteosynthesis in distal tibial fractures. Journal of Investigative Surgery 2012;25(5):326‐9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Zou 2013 {published data only}
-
- Zou J, Zhang W, Zhang CQ. Comparison of minimally invasive percutaneous plate osteosynthesis with open reduction and internal fixation for treatment of extra‐articular distal tibia fractures. Injury 2013;44(8):1102‐6. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
References to ongoing studies
ISRCTN99771224 {unpublished data only}
-
- Costa M. UK FixDT: Fixation of distal tibia fractures. www.isrctn.com/ISRCTN99771224 (accessed 6 March 2015).
NCT01047826 {unpublished data only}
-
- AL‐Rumaih HA, Taha WS. M.I.P.O. vs intramedullary nailing in tibia fractures (MINT). http://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01047826?term=NCT01047826&rank=1 (accessed 19 March 2015).
Additional references
Ahmad 2010
-
- Ahmad MA, Sivaraman A, Zia A, Rai A, Patel AD. Percutaneous locking plates for fractures of the distal tibia: our experience and a review of the literature. Journal of Trauma 2012; Vol. 72, issue 2:E81‐7. - PubMed
AO/OTA 1996
-
- No authors listed. Fracture and dislocation compendium: Orthopaedic Trauma Association Committee for Coding and Classification. Journal of Orthopaedic Trauma 1996;10(Suppl 1):1‐154. - PubMed
Babis 1997
-
- Babis GC, Vayanos ED, Papaioannou N, Pantazopoulos T. Results of surgical treatment of tibial plafond fractures. Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research 1997;(341):99‐105. - PubMed
Bedi 2006
-
- Bedi A, Le TT, Karunakar MA. Surgical treatment of nonarticular distal tibia fractures. Journal of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons 2006;14(7):406‐16. - PubMed
Blauth 2001
-
- Blauth M, Bastian L, Krettek C, Knop C, Evans S. Surgical options for the treatment of severe tibial pilon fractures: a study of three techniques. Journal of Orthopaedic Trauma 2001;15(3):153‐60. - PubMed
Borelli 2002
-
- Borrelli J, Prickett W, Song E, Becker D, Ricci W. Extra osseous blood supply of the distal tibia and the effects of different plating techniques: human cadaveric study. Journal of Orthopaedic Trauma 2002;16(10):691‐5. - PubMed
Collinge 2010
-
- Collinge C, Protzman R. Outcome of minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis for metaphyseal distal tibia fractures. Journal of Orthopaedic Trauma 2010;24(1):24‐9. - PubMed
Court‐Brown 1990
-
- Court‐Brown CM, Christie J, McQueen MM. Closed intramedullary tibial nailing. Its use in closed and type I open fractures. Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery. British Volume 1990;72(4):605‐11. - PubMed
Court‐Brown 1995
-
- Court‐Brown CM, McBirnie J. The epidemiology of tibial fractures. Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery. British Volume 1995;77(3):417‐21. - PubMed
Court‐Brown 1997
-
- Court‐Brown CM, Gustilo T, Shaw AD. Knee pain after intramedullary tibial nailing: its incidence, etiology, and outcome. Journal of Orthopaedic Trauma 1997;11(2):103‐5. - PubMed
Court‐Brown 2005
-
- Court‐Brown CM. Fractures of the tibia and fibula. In: Bucholz R, Heckman J, Court‐Brown C, et al. editor(s). Rockwood and Green's fractures in adults. 6th Edition. Vol. 2, Philadelphia: Lippincott Wiliams & Wilkins, 2005:2079‐146.
Court‐Brown 2006
-
- Court‐Brown CM, Caesar B. Epidemiology of adult fractures: a review. Injury 2006;37(8):691‐7. - PubMed
Digby 1982
-
- Digby JM, Holloway GMN, Webb JK. A study of function after tibial cast bracing. Injury 1982;14(5):432‐9. - PubMed
Egger 1997
Haines 1984
-
- Haines JF, Williams EA, Hargadon ES, Davies DR. Is conservative treatment of displaced tibial shaft fractures justified?. Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery. British Volume 1984;66(1):84‐8. - PubMed
Hasenboehler 2007
-
- Hasenboehler E, Rikli D, Babst R. Locking compression plate with minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis in diaphyseal and distal tibial fracture: a retrospective study of 32 patients. Injury 2007;38(3):365‐70. - PubMed
Higgins 2003
Higgins 2004
-
- Higgins JP, Thompson SG. Controlling the risk of spurious findings from meta‐regression. Statistics in Medicine 2004;23(11):1663‐82. - PubMed
Higgins 2011
-
- Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Kitaoka 1994
-
- Kitaoka HB, Alexander IJ, Adelaar RS, Nunley JA, Myerson MS, Sanders M. Clinical rating systems for the ankle, hindfoot, midfoot, hallux, and lesser toes. Foot and Ankle International 1994;15(7):349‐53. - PubMed
Kwok 2014
-
- Kwok CS, Crossman PT, Loizou CL. Plate versus nail for distal tibial fractures: a systematic review and meta‐analysis. Journal of Orthopaedic Trauma 2014;28(9):542‐8. - PubMed
Lefebvre 2011
-
- Lefebvre C, Manheimer E, Glanville J. Chapter 6: Searching for studies. In: Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Mast 1988
-
- Mast JW, Spiegel PG, Pappas JN. Fractures of the tibial pilon. Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research 1988;(230):68‐82. - PubMed
Mosheiff 1999
-
- Mosheiff R, Safran O, Segal D, Liebergall M. The unreamed tibial nail in the treatment of distal metaphyseal fractures. Injury 1999;30(2):83‐90. - PubMed
Müller 1990
-
- Müller ME, Nezarian S, Koch P, Schatzker J. The Comprehensive Classification of Fractures of Long Bones. Berlin, Germany: Springer‐Verlag, 1990.
Obremskey 2004
-
- Obremskey WT, Medina M. Comparison of intramedullary nailing of distal third tibial shaft fractures: before and after traumatologists. Orthopedics 2004;27(11):1180‐4. - PubMed
Oestern 1984
-
- Oestern H‐J, Tscherne H. Pathophysiology and classification of soft tissue injuries associated with fractures. In: Tscherne H, Gotzen L editor(s). Fractures with Soft Tissue Injuries. Springer‐Verlag, 1984:1‐9.
Olerud 1984
-
- Olerud C, Molander H. A scoring scale for symptomatic evaluation after ankle fracture. Archives of Orthopaedic and Trauma Surgery 1984;103(3):190–4. - PubMed
Ovadia 1986
-
- Ovadia DN, Beals RK. Fractures of the tibial plafond. Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery. American Volume 1986;68:543‐51. - PubMed
Petrisor 2010
-
- Petrisor BA, Bhandari M, Schemitsch E. Tibia and fibula fractures. Rockwood And Green's Fractures In Adults. 7th Edition. Vol. 2, Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2010.
Redfern 2004
-
- Redfern DJ, Syed SU, Davies SJM. Fractures of the distal tibia: minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis. Injury 2004;35(6):615‐20. - PubMed
RevMan 2014 [Computer program]
-
- Review Manager (RevMan) Version 5.3. Copenhagen: The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2014.
Robinson 1995
-
- Robinson CM, McLauchlan GJ, McLean IP, Court‐Brown CM. Distal metaphyseal fractures of the tibia with minimal involvement of the ankle: classification and treatment by locked intramedullary nailing. Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery. British Volume 1995;77(5):781‐7. - PubMed
Toivanen 2002
-
- Toivanen JA, Väistö O, Kannus P, Latvala K, Honkonen SE, Järvinen MJ. Anterior knee pain after intramedullary nailing of fractures of the tibial shaft: a prospective, randomized study comparing two different nail‐insertion techniques. Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery. American Volume 2002;84(4):580‐5. - PubMed
Wagner 2003
-
- Wagner M. General principles for the clinical use of the LCP. Injury 2003;34(Suppl 2):B31‐42. - PubMed
Whittle 2008
-
- Whittle AP. Fractures of the lower extremity. In: Canale ST, Beatty JH editor(s). Campbell's Operative Orthopaedics. 11th Edition. Vol. 3, Philadelphia: Mosby, Elsevier, 2008. [ISBN: 9780323033299]
Xue 2014
-
- Xue XH, Yan SG, Cai XZ, Shi MM, Lin T. Intramedullary nailing versus plating for extra‐articular distal tibial metaphyseal fracture: a systematic review and meta‐analysis. Injury 2014;45(4):667‐76. - PubMed
Zelle 2006
-
- Zelle BA, Bhandari M, Espiritu M, Koval KJ, Zlowodzki M. Evidence‐Based Orthopaedic Trauma Working Group. Treatment of distal tibia fractures without articular involvement: a systematic review of 1125 fractures. Journal of Orthopaedic Trauma 2006;20(1):76‐9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

