Sequence variation within the KIV-2 copy number polymorphism of the human LPA gene in African, Asian, and European populations
- PMID: 25822457
- PMCID: PMC4378929
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0121582
Sequence variation within the KIV-2 copy number polymorphism of the human LPA gene in African, Asian, and European populations
Abstract
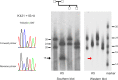
Amazingly little sequence variation is reported for the kringle IV 2 copy number variation (KIV 2 CNV) in the human LPA gene. Apart from whole genome sequencing projects, this region has only been analyzed in some detail in samples of European populations. We have performed a systematic resequencing study of the exonic and flanking intron regions within the KIV 2 CNV in 90 alleles from Asian, European, and four different African populations. Alleles have been separated according to their CNV length by pulsed field gel electrophoresis prior to unbiased specific PCR amplification of the target regions. These amplicons covered all KIV 2 copies of an individual allele simultaneously. In addition, cloned amplicons from genomic DNA of an African individual were sequenced. Our data suggest that sequence variation in this genomic region may be higher than previously appreciated. Detection probability of variants appeared to depend on the KIV 2 copy number of the analyzed DNA and on the proportion of copies carrying the variant. Asians had a high frequency of so-called KIV 2 type B and type C (together 70% of alleles), which differ by three or two synonymous substitutions respectively from the reference type A. This is most likely explained by the strong bottleneck suggested to have occurred when modern humans migrated to East Asia. A higher frequency of variable sites was detected in the Africans. In particular, two previously unreported splice site variants were found. One was associated with non-detectable Lp(a). The other was observed at high population frequencies (10% to 40%). Like the KIV 2 type B and C variants, this latter variant was also found in a high proportion of KIV 2 repeats in the affected alleles and in alleles differing in copy numbers. Our findings may have implications for the interpretation of SNP analyses in other repetitive loci of the human genome.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
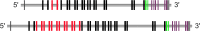



Similar articles
-
Lipoprotein(a) beyond the kringle IV repeat polymorphism: The complexity of genetic variation in the LPA gene.Atherosclerosis. 2022 May;349:17-35. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2022.04.003. Atherosclerosis. 2022. PMID: 35606073 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comprehensive analysis of genomic variation in the LPA locus and its relationship to plasma lipoprotein(a) in South Asians, Chinese, and European Caucasians.Circ Cardiovasc Genet. 2010 Feb;3(1):39-46. doi: 10.1161/CIRCGENETICS.109.907642. Epub 2009 Dec 30. Circ Cardiovasc Genet. 2010. PMID: 20160194
-
LPA and PLG sequence variation and kringle IV-2 copy number in two populations.Hum Hered. 2008;66(4):199-209. doi: 10.1159/000143403. Epub 2008 Jul 9. Hum Hered. 2008. PMID: 18612205 Free PMC article.
-
Lack of association of rs3798220 with small apolipoprotein(a) isoforms and high lipoprotein(a) levels in East and Southeast Asians.Atherosclerosis. 2015 Oct;242(2):521-8. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2015.07.015. Epub 2015 Jul 15. Atherosclerosis. 2015. PMID: 26302166
-
Lipoprotein (a): impact by ethnicity and environmental and medical conditions.J Lipid Res. 2016 Jul;57(7):1111-25. doi: 10.1194/jlr.R051904. Epub 2015 Dec 4. J Lipid Res. 2016. PMID: 26637279 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular, Population, and Clinical Aspects of Lipoprotein(a): A Bridge Too Far?J Clin Med. 2019 Nov 27;8(12):2073. doi: 10.3390/jcm8122073. J Clin Med. 2019. PMID: 31783529 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Analysis of five deep-sequenced trio-genomes of the Peninsular Malaysia Orang Asli and North Borneo populations.BMC Genomics. 2019 Nov 12;20(1):842. doi: 10.1186/s12864-019-6226-8. BMC Genomics. 2019. PMID: 31718558 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of Apolipoprotein(a) Isoform Size Using Phenotypic and Genotypic Methods.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Sep 9;24(18):13886. doi: 10.3390/ijms241813886. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37762189 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lipoprotein(a) beyond the kringle IV repeat polymorphism: The complexity of genetic variation in the LPA gene.Atherosclerosis. 2022 May;349:17-35. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2022.04.003. Atherosclerosis. 2022. PMID: 35606073 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A comprehensive map of single-base polymorphisms in the hypervariable LPA kringle IV type 2 copy number variation region.J Lipid Res. 2019 Jan;60(1):186-199. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M090381. Epub 2018 Nov 9. J Lipid Res. 2019. PMID: 30413653 Free PMC article.
References
-
- McLean JW, Tomlinson JE, Kuang WJ, Eaton DL, Chen EY, Fless GM, et al. cDNA sequence of human apolipoprotein(a) is homologous to plasminogen. Nature. 1987; 330: 132–137. - PubMed
-
- White AL, Guerra B, Lanford RE. Influence of allelic variation on apolipoprotein(a) folding in the endoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1997; 272: 5048–5055. - PubMed
-
- Brunner C, Lobentanz EM, Petho-Schramm A, Ernst A, Kang C, Dieplinger H, et al. The number of identical kringle IV repeats in apolipoprotein(a) affects its processing and secretion by HepG2 cells. J Biol Chem. 1996; 271: 32403–32410. - PubMed
-
- Sandholzer C, Hallman DM, Saha N, Sigurdsson G, Lackner C, Császár A, et al. Effects of the apolipoprotein(a) size polymorphism on the lipoprotein(a) concentration in 7 ethnic groups. Hum Genet. 1991; 86: 607–614. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

