Effects of cyclic tensile strain on chondrocyte metabolism: a systematic review
- PMID: 25822615
- PMCID: PMC4379081
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0119816
Effects of cyclic tensile strain on chondrocyte metabolism: a systematic review
Abstract
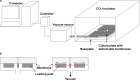
Chondrocytes reorganize the extracellular matrix of articular cartilage in response to externally applied loads. Thereby, different loading characteristics lead to different biological responses. Despite of active research in this area, it is still unclear which parts of the extracellular matrix adapt in what ways, and how specific loading characteristics affect matrix changes. This review focuses on the influence of cyclic tensile strain on chondrocyte metabolism in vitro. It also aimed to identify anabolic or catabolic chondrocyte responses to different loading protocols. The key findings show that loading cells up to 3% strain, 0.17 Hz, and 2 h, resulted in weak or no biological responses. Loading between 3-10% strain, 0.17-0.5 Hz, and 2-12 h led to anabolic responses; and above 10% strain, 0.5 Hz, and 12 h catabolic events predominated. However, this review also discusses that various other factors are involved in the remodeling of the extracellular matrix in response to loading, and that parameters like an inflammatory environment might influence the biological response.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Wilkins RJ, Browning JA, Urban JP. Chondrocyte regulation by mechanical load. Biorh. 2000; 37: 67–74. - PubMed
-
- Urban J. The chondrocyte: a cell under pressure. Rheumatology. 1994; 33: 901–908. - PubMed
-
- Grodzinsky AJ, Levenston ME, Jin M, Frank EH. Cartilage tissue remodeling in response to mechanical forces. Annu Rev Biomed Eng. 2000; 2: 691–713. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

