An integrated analysis of the effects of microRNA and mRNA on esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
- PMID: 25823933
- PMCID: PMC4438920
- DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2015.3557
An integrated analysis of the effects of microRNA and mRNA on esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
Abstract
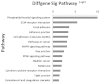
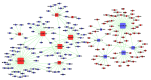
Esophageal squamous cell cancer (ESCC) is an aggressive type of cancer with poor prognosis and leading to decreased quality of life. The identification of patients at increased risk of esophageal squamous cell cancer may improve current understanding of the role of micro (mi)RNA in tumorigenesis, since the miRNA pattern of these patients may be associated with tumorigenesis. In the present study, the miRNA and mRNA expression profiles of ESCC tissue samples and adjacent normal control tissue samples were obtained from two dependent GEO series. Bioinformatics analyses, including the use of the Gene Oncology and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes databases, were used to identify genes and pathways, which were specifically associated with miRNA-associated ESCC oncology. A total of 17 miRNAs and 1,670 probes were differentially expressed in the two groups, and the differentially expressed miRNA and target interactions were analyzed. The mRNA of miRNA target genes were found to be involve 49 GO terms and 14 pathways. Of the genes differentially expressed between the two groups, miRNA-181a, miRNA-202, miRNA-155, FNDC3B, BNC2 and MBD2 were the most significantly altered and may be important in the regulatory network. In the present study, a novel pattern of differential miRNA-target expression was constructed, which with further investigation, may provide novel targets for diagnosing and understanding the mechanism of ESCC.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Integrated microRNA-mRNA analysis revealing the potential roles of microRNAs in tongue squamous cell cancer.Mol Med Rep. 2015 Jul;12(1):885-94. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2015.3467. Epub 2015 Mar 11. Mol Med Rep. 2015. PMID: 25760063 Free PMC article.
-
Novel miRNA markers and their mechanism of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) based on TCGA.Sci Rep. 2024 Nov 8;14(1):27261. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-76321-0. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39516222 Free PMC article.
-
The global expression profiling in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.Genomics. 2017 Jul;109(3-4):241-250. doi: 10.1016/j.ygeno.2017.04.005. Epub 2017 Apr 22. Genomics. 2017. PMID: 28442363
-
MicroRNAs in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: Potential biomarkers and therapeutic targets.Cancer Biomark. 2017;19(1):1-9. doi: 10.3233/CBM-160240. Cancer Biomark. 2017. PMID: 28269750 Review.
-
MicroRNAs in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: Application in prognosis, diagnosis, and drug delivery.Pathol Res Pract. 2022 Dec;240:154196. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2022.154196. Epub 2022 Nov 2. Pathol Res Pract. 2022. PMID: 36356334 Review.
Cited by
-
FNDC3B promotes cell migration and tumor metastasis in hepatocellular carcinoma.Oncotarget. 2016 Aug 2;7(31):49498-49508. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.10374. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27385217 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of More Feasible MicroRNA-mRNA Interactions within Multiple Cancers Using Principal Component Analysis Based Unsupervised Feature Extraction.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 May 10;17(5):696. doi: 10.3390/ijms17050696. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27171078 Free PMC article.
-
NS5ABP37 inhibits liver cancer by impeding lipogenesis and cholesterogenesis.Cancer Sci. 2017 Jan;108(1):12-22. doi: 10.1111/cas.13117. Cancer Sci. 2017. PMID: 27862769 Free PMC article.
-
Esophageal Cancer Development: Crucial Clues Arising from the Extracellular Matrix.Cells. 2020 Feb 17;9(2):455. doi: 10.3390/cells9020455. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32079295 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SH3BGRL2 inhibits growth and metastasis in clear cell renal cell carcinoma via activating hippo/TEAD1-Twist1 pathway.EBioMedicine. 2020 Jan;51:102596. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2019.12.005. Epub 2020 Jan 6. EBioMedicine. 2020. PMID: 31911271 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

