Update on the autoimmune pathology of multiple sclerosis: B-cells as disease-drivers and therapeutic targets
- PMID: 25824054
- PMCID: PMC4401636
- DOI: 10.1159/000377675
Update on the autoimmune pathology of multiple sclerosis: B-cells as disease-drivers and therapeutic targets
Abstract
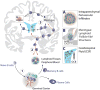
Background: Collectively, research on the role of B-cells in the pathogenesis of multiple sclerosis (MS) illustrates how translational medicine has given rise to promising therapeutic approaches for one of the most debilitating chronic neurological diseases in young adults. First described in 1935, the experimental autoimmune/allergic encephalomyelitis model is a key animal model that has provided the foundation for important developments in targeted therapeutics.
Summary: While additional B-cell therapies for MS are presently being developed by the pharmaceutical industry, much remains to be understood about the role played by B-cells in MS. The goal of this review is to summarize how B-cells may contribute to MS pathogenesis and thereby provide a basis for understanding why B-cell depletion is so effective in the treatment of this disease. Key Messages: B-cells are key players in the pathogenesis of MS, and their depletion via B-cell-targeted therapy ameliorates disease activity.
Clinical implications: In 2008, data from the first CD20-targeting B-cell depleting therapeutic trials using rituximab in MS were published. Since then, there has been a large body of evidence demonstrating the effectiveness of B-cell depletion mediated via anti-CD20 antibodies. Intense research efforts focusing on the immunopathological relevance of B-cells has gained significant momentum and given rise to a constellation of promising therapeutic agents for this complex B-cell-driven disease, including novel anti-CD20 antibodies, as well as agents targeting CD19 and BAFF-R.
© 2015 S. Karger AG, Basel.
Figures


References
-
- Compston A, Coles A. Multiple sclerosis. Lancet. 2008;372:1502–1517. - PubMed
-
- Orton SM, Herrera BM, Yee IM, et al. Sex ratio of multiple sclerosis in canada: A longitudinal study. Lancet neurology. 2006;5:932–936. - PubMed
-
- Hauser SL, Oksenberg JR. The neurobiology of multiple sclerosis: Genes, inflammation, and neurodegeneration. Neuron. 2006;52:61–76. - PubMed
-
- Bar-Or A, Calabresi PA, Arnold D, et al. Rituximab in relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis: A 72-week, open-label, phase i trial. Annals of neurology. 2008;63:395–400. - PubMed
-
- Hauser SL, Waubant E, Arnold DL, et al. B-cell depletion with rituximab in relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis. N Engl J Med. 2008;358:676–688. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

