Role of Rhizomys pruinosus as a natural animal host of Penicillium marneffei in Guangdong, China
- PMID: 25824250
- PMCID: PMC4476820
- DOI: 10.1111/1751-7915.12275
Role of Rhizomys pruinosus as a natural animal host of Penicillium marneffei in Guangdong, China
Abstract
Penicillium marneffei, a dimorphic fungus that can cause penicilliosis marneffei, is endemic in Southeast Asia. The only known hosts of P. marneffei are humans and bamboo rats. The aim of our study was to explore the distribution of P. marneffei in bamboo rats, their associated environment and non-rat-associated environments. Totally, 270 samples were collected in Guangdong province of China in 2012; the prevalence of P. marneffei was much higher in samples collected from surrounding areas of burrows (8.2%) than in the samples obtained from non-rat-associated sites (2%) or artificial farms of bamboo rats (0%). There was no difference in P. marneffei isolated rate from different areas of Guangdong province. The infection is prevalent in all rats, and this fungus could be frequently seen in the rats' lungs. This study confirms that bamboo rat is the ecological niche of P. marneffei and hypothesizes that bamboo rats become infected by inhaling aerosolized conidia originating from environmental sources, rather than by the fecal-oral route or transplacental crossing. According to the result of no detection of P. marneffei in the artificial farm, the activity of bamboo rats might be more relevant to the distribution and dissemination of P. marneffei in natural environment.
© 2015 The Authors. Microbial Biotechnology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd and Society for Applied Microbiology.
Figures

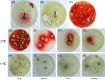
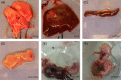
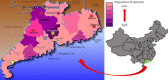
References
-
- Chariyalertsak S, Vanittanakom P, Nelson KE, Sirisanthana T. Vanittanakom N. Rhizomys sumatrensis and Cannomysbadius, new natural animal hosts of Penicillium marneffei. J Med Vet Mycol. 34:105–110. - PubMed
-
- Chariyalertsak S, Sirisanthana T, Supparatpinyo K. Nelson KE. Seasonal variation of disseminated Penicillium marneffei infections in northern Thailand: a clue to the reservoir? J Infect Dis. 1996a;173:1490–1493. - PubMed
-
- Chariyalertsak S, Sirisanthana T, Supparatpinyo K, Praparattanapan J. Nelson KE. Case-control study of risk factors for Penicillium marneffei infection in human immunodeficiency virus-infected patients in northern Thailand. Clin Infect Dis. 1997;24:1080–1086. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

