Fronto-Parietal Network Reconfiguration Supports the Development of Reasoning Ability
- PMID: 25824536
- PMCID: PMC4830293
- DOI: 10.1093/cercor/bhv050
Fronto-Parietal Network Reconfiguration Supports the Development of Reasoning Ability
Abstract
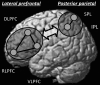
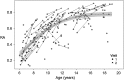
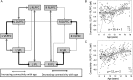
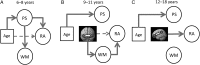
The goal of this fMRI study was to examine how well developmental improvements in reasoning ability can be explained by changes in functional connectivity between specific nodes in prefrontal and parietal cortices. To this end, we examined connectivity within the lateral fronto-parietal network (LFPN) and its relation to reasoning ability in 132 children and adolescents aged 6-18 years, 56 of whom were scanned twice over the course of 1.5 years. Developmental changes in strength of connections within the LFPN were most prominent in late childhood and early adolescence. Reasoning ability was related to functional connectivity between left rostrolateral prefrontal cortex (RLPFC) and inferior parietal lobule (IPL), but only among 12-18-year olds. For 9-11-year olds, reasoning ability was most strongly related to connectivity between left and right RLPFC; this relationship was mediated by working memory. For 6-8-year olds, significant relationships between connectivity and performance were not observed; in this group, processing speed was the primary mediator of improvement in reasoning ability. We conclude that different connections best support reasoning at different points in development and that RLPFC-IPL connectivity becomes an important predictor of reasoning during adolescence.
Keywords: adolescent; child; development; dorsolateral; functional connectivity; inferior parietal lobule; parietal cortex; prefrontal cortex; processing speed; reasoning; rostrolateral; working memory.
© The Author 2015. Published by Oxford University Press. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures

References
-
- Badre D, D'Esposito M. 2007. Functional magnetic resonance imaging evidence for a hierarchical organization of the prefrontal cortex. J Cogn Neurosci. 19(12):2082–2099. - PubMed
-
- Boorman ED, Behrens TEJ, Woolrich MW, Rushworth MFS. 2009. How green is the grass on the other side? Frontopolar cortex and the evidence in favor of alternative courses of action. Neuron. 62(5):733–743. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

