Glycopeptide analogues of PSGL-1 inhibit P-selectin in vitro and in vivo
- PMID: 25824568
- PMCID: PMC4423566
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms7387
Glycopeptide analogues of PSGL-1 inhibit P-selectin in vitro and in vivo
Abstract
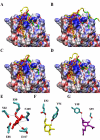
Blockade of P-selectin (P-sel)/PSGL-1 interactions holds significant potential for treatment of disorders of innate immunity, thrombosis and cancer. Current inhibitors remain limited due to low binding affinity or by the recognized disadvantages inherent to chronic administration of antibody therapeutics. Here we report an efficient approach for generating glycosulfopeptide mimics of N-terminal PSGL-1 through development of a stereoselective route for multi-gram scale synthesis of the C2 O-glycan building block and replacement of hydrolytically labile tyrosine sulfates with isosteric sulfonate analogues. Library screening afforded a compound of exceptional stability, GSnP-6, that binds to human P-sel with nanomolar affinity (Kd~22 nM). Molecular dynamics simulation defines the origin of this affinity in terms of a number of critical structural contributions. GSnP-6 potently blocks P-sel/PSGL-1 interactions in vitro and in vivo and represents a promising candidate for the treatment of diseases driven by acute and chronic inflammation.
Figures




References
-
- Kolaczkowska E, Kubes P. Neutrophil recruitment and function in health and inflammation. Nature reviews. Immunology. 2013;13:159–175. - PubMed
-
- Ley K, Laudanna C, Cybulsky MI, Nourshargh S. Getting to the site of inflammation: The leukocyte adhesion cascade updated. Nat Rev Immunol. 2007;7:678–689. - PubMed
-
- Palabrica T, et al. Leukocyte accumulation promoting fibrin deposition is mediated in vivo by P-selectin on adherent platelets. Nature. 1992;359:848–851. - PubMed
-
- Mayadas TN, Johnson RC, Rayburn H, Hynes RO, Wagner DD. Leukocyte rolling and extravasation are severely compromised in P selectin-deficient mice. Cell. 1993;74:541–554. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 HL106018/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL106018/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI047294/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI047294/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM094919/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- HL085607/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P41 GM103390/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- GM103694/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL085607/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P41 GM103694/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- GM094919/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- GM103390/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL128237/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- DK069275/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 GM116196/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- HL60963/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK069275/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

