Glycosylation of immunoglobulin G determines osteoclast differentiation and bone loss
- PMID: 25825024
- PMCID: PMC4389255
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms7651
Glycosylation of immunoglobulin G determines osteoclast differentiation and bone loss
Abstract
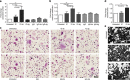
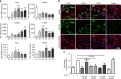
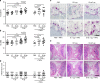
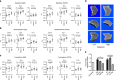
Immunglobulin G (IgG) sialylation represents a key checkpoint that determines the engagement of pro- or anti-inflammatory Fcγ receptors (FcγR) and the direction of the immune response. Whether IgG sialylation influences osteoclast differentiation and subsequently bone architecture has not been determined yet, but may represent an important link between immune activation and bone loss. Here we demonstrate that desialylated, but not sialylated, immune complexes enhance osteoclastogenesis in vitro and in vivo. Furthermore, we find that the Fc sialylation state of random IgG and specific IgG autoantibodies determines bone architecture in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. In accordance with these findings, mice treated with the sialic acid precursor N-acetylmannosamine (ManNAc), which results in increased IgG sialylation, are less susceptible to inflammatory bone loss. Taken together, our findings provide a novel mechanism by which immune responses influence the human skeleton and an innovative treatment approach to inhibit immune-mediated bone loss.
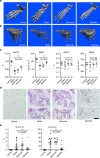
Figures

Comment in
-
Osteoimmunology: IgG immune complexes directly regulate bone homeostasis.Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2015 May;11(5):257. doi: 10.1038/nrrheum.2015.51. Epub 2015 Apr 14. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2015. PMID: 25868492 No abstract available.
References
-
- Arnold J. N., Wormald M. R., Sim R. B., Rudd P. M. & Dwek R. A. The impact of glycosylation on the biological function and structure of human immunoglobulins. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 25, 21–50 (2007) . - PubMed
-
- Anthony R. M. & Nimmerjahn F. The role of differential IgG glycosylation in the interaction of antibodies with FcgammaRs in vivo. Curr. Opin. Organ Transplant. 16, 7–14 (2011) . - PubMed
-
- Yamaguchi Y. et al.. Glycoform-dependent conformational alteration of the Fc region of human immunoglobulin G1 as revealed by NMR spectroscopy. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1760, 693–700 (2006) . - PubMed
-
- Bohm S., Schwab I., Lux A. & Nimmerjahn F. The role of sialic acid as a modulator of the anti-inflammatory activity of IgG. Semin. Immunopathol. 34, 443–453 (2012) . - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

