Long-lasting partnership between insulin resistance and endothelial dysfunction: role of metabolic memory
- PMID: 25825057
- PMCID: PMC4543609
- DOI: 10.1111/bph.13145
Long-lasting partnership between insulin resistance and endothelial dysfunction: role of metabolic memory
Abstract
Background and purpose: The persistence of deleterious effects of hyperglycaemia even after glucose normalization is referred to as 'metabolic memory'. However, similar persistent effects of the metabolic consequences of a high fat diet (HFD) have not been described.
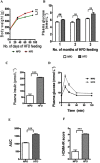
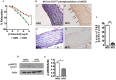
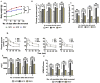
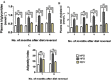
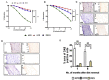
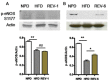
Experimental approach: Rats were given a normal pellet diet (NPD) or a HFD for 3 months. The animals from the HFD group were then returned to the NPD to observe the long-term effects of insulin resistance. Endothelial dysfunction was assessed by carbachol-mediated vasorelaxation and eNOS phosphorylation.
Key results: As expected, HFD consumption resulted in insulin resistance and endothelial dysfunction. Phosphorylation of eNOS at S1177 was decreased in HFD rats, compared with that in the NPD group. Rats on 3 months of HFD showed glucose intolerance and impaired insulin sensitivity and were then switched back to NPD (REV group) . Levels of cholesterol and triglyceride, and adiposity returned to normal in REV rats. However, endothelium-dependent vascular responses to carbachol which were impaired in HFD rats, continued to be impaired in REV rats. Similarly, decreased eNOS phosphorylation after HFD was not improved after 1 or 6 months of REV.
Conclusions and implications: Our data indicate that returning to NPD did not improve the insulin sensitivity or the endothelial dysfunction induced by HFD. Although some biochemical parameters responsible for insulin resistance and endothelial dysfunction were normalized, molecular and vascular abnormalities, involving NO, persisted for several months, highlighting the long-lasting effects of metabolic memory.
© 2015 The British Pharmacological Society.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effect of tempol on altered angiotensin II and acetylcholine-mediated vascular responses in thoracic aorta isolated from rats with insulin resistance.Pharmacol Res. 2006 Mar;53(3):209-15. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2005.11.002. Epub 2006 Jan 10. Pharmacol Res. 2006. PMID: 16412660
-
Combination of high-fat diet-fed and low-dose streptozotocin-treated rat: a model for type 2 diabetes and pharmacological screening.Pharmacol Res. 2005 Oct;52(4):313-20. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2005.05.004. Pharmacol Res. 2005. PMID: 15979893
-
Decrease in myostatin by ladder-climbing training is associated with insulin resistance in diet-induced obese rats.Chin Med J (Engl). 2014;127(12):2342-9. Chin Med J (Engl). 2014. PMID: 24931254
-
PPAR gamma agonists partially restores hyperglycemia induced aggravation of vascular dysfunction to angiotensin II in thoracic aorta isolated from rats with insulin resistance.Pharmacol Res. 2007 May;55(5):400-7. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2007.01.015. Epub 2007 Feb 2. Pharmacol Res. 2007. PMID: 17369046
-
DPP4-inhibitor improves neuronal insulin receptor function, brain mitochondrial function and cognitive function in rats with insulin resistance induced by high-fat diet consumption.Eur J Neurosci. 2013 Mar;37(5):839-49. doi: 10.1111/ejn.12088. Epub 2012 Dec 12. Eur J Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23240760
Cited by
-
Metformin Improves Metabolic Memory in High Fat Diet (HFD)-induced Renal Dysfunction.J Biol Chem. 2016 Oct 14;291(42):21848-21856. doi: 10.1074/jbc.C116.732990. Epub 2016 Aug 22. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 27551045 Free PMC article.
-
The Legacy Effect in the Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease.Nutrients. 2020 Oct 22;12(11):3227. doi: 10.3390/nu12113227. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 33105611 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Old and New Biomarkers Associated with Endothelial Dysfunction in Chronic Hyperglycemia.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021 Dec 27;2021:7887426. doi: 10.1155/2021/7887426. eCollection 2021. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021. PMID: 34987703 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metformin in cardiovascular diabetology: a focused review of its impact on endothelial function.Theranostics. 2021 Sep 9;11(19):9376-9396. doi: 10.7150/thno.64706. eCollection 2021. Theranostics. 2021. PMID: 34646376 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Triglyceride-glucose index trajectory and stroke incidence in patients with hypertension: a prospective cohort study.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2022 Jul 27;21(1):141. doi: 10.1186/s12933-022-01577-7. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2022. PMID: 35897017 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arcaro G, Cretti A, Balzano S, Lechi A, Muggeo M, Bonora E, et al. Insulin causes endothelial dysfunction in humans sites and mechanisms. Circulation. 2002;105:576–582. - PubMed
-
- Bakker W, Eringa EC, Sipkema P, Van Hinsbergh VWM. Endothelial dysfunction and diabetes: roles of hyperglycemia, impaired insulin signaling and obesity. Cell Tissue Res. 2009;335:165–189. - PubMed
-
- Bauersachs J, Schafer A. Tetrahydrobiopterin and eNOS dimer/monomer ratio – a clue to eNOS uncoupling in diabetes? Cardiovasc Res. 2005;65:768–769. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

