High-sensitivity cardiac troponin I and B-type natriuretic Peptide as predictors of vascular events in primary prevention: impact of statin therapy
- PMID: 25825410
- PMCID: PMC4444427
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.114.014522
High-sensitivity cardiac troponin I and B-type natriuretic Peptide as predictors of vascular events in primary prevention: impact of statin therapy
Abstract
Background: Cardiac troponin and B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP) concentrations are associated with adverse cardiovascular outcome in primary prevention populations. Whether statin therapy modifies this association is poorly understood.
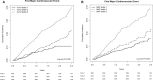
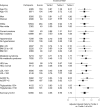
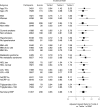
Methods and results: We measured high-sensitivity cardiac troponin I (hsTnI) in 12 956 and BNP in 11 076 participants without cardiovascular disease in the Justification for the Use of Statins in Prevention: An Intervention Trial Evaluating Rosuvastatin (JUPITER) trial before randomization to rosuvastatin 20 mg/d or placebo. Nearly 92% of participants had detectable circulating hsTnI, and 2.9% of men and 4.1% of women had levels above proposed sex-specific reference limits of 36 and 15 ng/L, respectively. hsTnI concentrations in the highest tertile were associated with a first major cardiovascular event (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR], 2.19; 95% confidence interval, 1.56-3.06; P for trend <0.001). BNP levels in the highest tertile were also associated a first cardiovascular event (aHR, 1.94; 95% confidence interval, 1.41-2.68; P for trend <0.001). The risk of all-cause mortality was elevated for the highest versus the lowest tertiles of hsTnI (aHR, 2.61; 95% confidence interval, 1.81-3.78; P for trend <0.001) and BNP (aHR, 1.45; 95% confidence interval, 1.03-2.04; P for trend 0.02). Rosuvastatin was equally effective in preventing a first cardiovascular event across categories of hsTnI (aHR range, 0.50-0.60) and BNP (aHR range, 0.42-0.67) with no statistically significant evidence of interaction (P for interaction=0.53 and 0.20, respectively).
Conclusions: In a contemporary primary prevention population, baseline cardiac troponin I and BNP were associated with the risk of vascular events and all-cause mortality. The benefits of rosuvastatin were substantial and consistent regardless of baseline hsTnI or BNP concentrations.
Clinical trial registration: URL: http://www.clinicaltrials.gov. Unique identifier: NCT00239681.
Keywords: hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA reductase inhibitors; natriuretic peptide, brain; primary prevention; troponin.
© 2015 The Authors.
Figures


References
-
- Thygesen K, Alpert JS, White HD Joint ESC/ACCF/AHA/WHF Task Force for the Redefinition of Myocardial Infarction. Universal definition of myocardial infarction. Eur Heart J. 2007;28:2525–2538. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehm355. - PubMed
-
- Everett BM, Cook NR, Magnone MC, Bobadilla M, Kim E, Rifai N, Ridker PM, Pradhan AD. Sensitive cardiac troponin T assay and the risk of incident cardiovascular disease in women with and without diabetes mellitus: the Women’s Health Study. Circulation. 2011;123:2811–2818. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.110.009928. - PMC - PubMed
-
- de Lemos JA, Drazner MH, Omland T, Ayers CR, Khera A, Rohatgi A, Hashim I, Berry JD, Das SR, Morrow DA, McGuire DK. Association of troponin T detected with a highly sensitive assay and cardiac structure and mortality risk in the general population. JAMA. 2010;304:2503–2512. doi: 10.1001/jama.2010.1768. - PMC - PubMed
-
- deFilippi CR, de Lemos JA, Christenson RH, Gottdiener JS, Kop WJ, Zhan M, Seliger SL. Association of serial measures of cardiac troponin T using a sensitive assay with incident heart failure and cardiovascular mortality in older adults. JAMA. 2010;304:2494–2502. doi: 10.1001/jama.2010.1708. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zeller T, Tunstall-Pedoe H, Saarela O, Ojeda F, Schnabel RB, Tuovinen T, Woodward M, Struthers A, Hughes M, Kee F, Salomaa V, Kuulasmaa K, Blankenberg S MORGAM Investigators. High population prevalence of cardiac troponin I measured by a high-sensitivity assay and cardiovascular risk estimation: the MORGAM Biomarker Project Scottish Cohort. Eur Heart J. 2014;35:271–281. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/eht406. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

