L1CAM/Neuroglian controls the axon-axon interactions establishing layered and lobular mushroom body architecture
- PMID: 25825519
- PMCID: PMC4384726
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.201407131
L1CAM/Neuroglian controls the axon-axon interactions establishing layered and lobular mushroom body architecture
Abstract
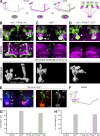
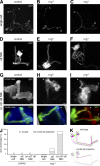
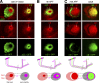
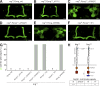
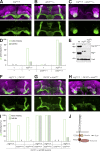
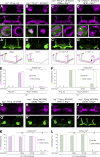
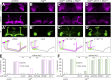
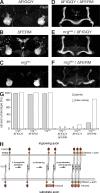
The establishment of neuronal circuits depends on the guidance of axons both along and in between axonal populations of different identity; however, the molecular principles controlling axon-axon interactions in vivo remain largely elusive. We demonstrate that the Drosophila melanogaster L1CAM homologue Neuroglian mediates adhesion between functionally distinct mushroom body axon populations to enforce and control appropriate projections into distinct axonal layers and lobes essential for olfactory learning and memory. We addressed the regulatory mechanisms controlling homophilic Neuroglian-mediated cell adhesion by analyzing targeted mutations of extra- and intracellular Neuroglian domains in combination with cell type-specific rescue assays in vivo. We demonstrate independent and cooperative domain requirements: intercalating growth depends on homophilic adhesion mediated by extracellular Ig domains. For functional cluster formation, intracellular Ankyrin2 association is sufficient on one side of the trans-axonal complex whereas Moesin association is likely required simultaneously in both interacting axonal populations. Together, our results provide novel mechanistic insights into cell adhesion molecule-mediated axon-axon interactions that enable precise assembly of complex neuronal circuits.
© 2015 Siegenthaler et al.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Drosophila L1CAM homolog Neuroglian signals through distinct pathways to control different aspects of mushroom body axon development.Development. 2011 Apr;138(8):1595-605. doi: 10.1242/dev.052787. Epub 2011 Mar 9. Development. 2011. PMID: 21389050 Free PMC article.
-
The L1-type cell adhesion molecule Neuroglian is necessary for maintenance of sensory axon advance in the Drosophila embryo.Neural Dev. 2008 Apr 8;3:10. doi: 10.1186/1749-8104-3-10. Neural Dev. 2008. PMID: 18397531 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic analysis of an overlapping functional requirement for L1- and NCAM-type proteins during sensory axon guidance in Drosophila.Mol Cell Neurosci. 2005 Jan;28(1):141-52. doi: 10.1016/j.mcn.2004.09.003. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2005. PMID: 15607949
-
Role of L1CAM for axon sprouting and branching.Cell Tissue Res. 2012 Jul;349(1):39-48. doi: 10.1007/s00441-012-1345-4. Epub 2012 Feb 28. Cell Tissue Res. 2012. PMID: 22370595 Review.
-
The L1CAM extracellular region: a multi-domain protein with modular and cooperative binding modes.Front Biosci. 2003 Sep 1;8:s1210-25. doi: 10.2741/1108. Front Biosci. 2003. PMID: 12957823 Review.
Cited by
-
The making of the Drosophila mushroom body.Front Physiol. 2023 Jan 13;14:1091248. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2023.1091248. eCollection 2023. Front Physiol. 2023. PMID: 36711013 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The ERM protein Moesin is essential for neuronal morphogenesis and long-term memory in Drosophila.Mol Brain. 2017 Aug 29;10(1):41. doi: 10.1186/s13041-017-0322-y. Mol Brain. 2017. PMID: 28851405 Free PMC article.
-
Long-Term Memory in Drosophila Is Influenced by Histone Deacetylase HDAC4 Interacting with SUMO-Conjugating Enzyme Ubc9.Genetics. 2016 Jul;203(3):1249-64. doi: 10.1534/genetics.115.183194. Epub 2016 May 6. Genetics. 2016. PMID: 27182943 Free PMC article.
-
To Stick or Not to Stick: The Multiple Roles of Cell Adhesion Molecules in Neural Circuit Assembly.Front Neurosci. 2022 Apr 28;16:889155. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2022.889155. eCollection 2022. Front Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35573298 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Alzheimer's Disease Associated Genes Ankyrin and Tau Cause Shortened Lifespan and Memory Loss in Drosophila.Front Cell Neurosci. 2019 Jun 11;13:260. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2019.00260. eCollection 2019. Front Cell Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31244615 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bieber A.J., Snow P.M., Hortsch M., Patel N.H., Jacobs J.R., Traquina Z.R., Schilling J., and Goodman C.S.. 1989. Drosophila neuroglian: a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily with extensive homology to the vertebrate neural adhesion molecule L1. Cell. 59:447–460 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90029-9 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

