Retinal blood vessels extraction using probabilistic modelling
- PMID: 25825666
- PMCID: PMC4376494
- DOI: 10.1186/2047-2501-2-2
Retinal blood vessels extraction using probabilistic modelling
Abstract
The analysis of retinal blood vessels plays an important role in detecting and treating retinal diseases. In this review, we present an automated method to segment blood vessels of fundus retinal image. The proposed method could be used to support a non-intrusive diagnosis in modern ophthalmology for early detection of retinal diseases, treatment evaluation or clinical study. This study combines the bias correction and an adaptive histogram equalisation to enhance the appearance of the blood vessels. Then the blood vessels are extracted using probabilistic modelling that is optimised by the expectation maximisation algorithm. The method is evaluated on fundus retinal images of STARE and DRIVE datasets. The experimental results are compared with some recently published methods of retinal blood vessels segmentation. The experimental results show that our method achieved the best overall performance and it is comparable to the performance of human experts.
Keywords: Expectation maximisation; Retinal images; Vessel segmentation.
Figures
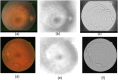



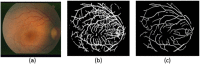
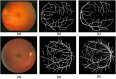
References
-
- Fritzsche K, Can A, Shen H, Tsai C, Turner J, Stewart C, Roysam B. Automated model based segmentation, tracing and analysis of retinal vasculature from digital fundus images. State-of-The-Art Angiography Appl Plaque Imaging Using MR, CT, Ultrasound X-rays. 2003;2003(6):225–298.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

