Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs) for the prevention of migraine in adults
- PMID: 25829028
- PMCID: PMC6513227
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD002919.pub3
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs) for the prevention of migraine in adults
Abstract
Background: This is an updated version of the original Cochrane review published in 2005 on selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) for preventing migraine and tension-type headache. The original review has been split in two parts and this review now only regards migraine prevention. Another updated review is under development to cover tension-type headache.Migraine is a common disorder. The chronic forms are associated with disability and have a high economic impact. In view of discoveries about the role of serotonin and other neurotransmitters in pain mechanisms, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs) have been evaluated for the prevention of migraine.
Objectives: To determine the efficacy and tolerability of SSRIs and SNRIs compared to placebo and other active interventions in the prevention of episodic and chronic migraine in adults.
Search methods: For the original review, we searched MEDLINE (1966 to January 2004), EMBASE (1994 to May 2003), the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL 2003, Issue 4), and Headache Quarterly (1990 to 2003). For this update, we applied a revised search strategy to reflect the broader type of intervention (SSRIs and SNRIs). We searched CENTRAL (2014, Issue 10), MEDLINE (1946 to November 2014), EMBASE (1980 to November 2014), and PsycINFO (1987 to November 2014). We also checked the reference lists of retrieved articles and searched trial registries for ongoing trials.
Selection criteria: We included randomised controlled trials comparing SSRIs or SNRIs with any type of control intervention in participants 18 years and older of either sex with migraine.
Data collection and analysis: Two authors independently extracted data (migraine frequency, index, intensity, and duration; use of symptomatic/analgesic medication; days off work; quality of life; mood improvement; cost-effectiveness; and adverse events) and assessed the risk of bias of trials. The primary outcome of this updated review is migraine frequency.
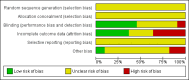
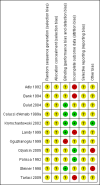
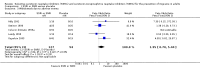
Main results: The original review included eight studies on migraine. Overall, we now include 11 studies on five SSRIs and one SNRI with a total of 585 participants. Six studies were placebo-controlled, four compared a SSRI or SNRI to amitriptyline, and one was a head-to-head comparison (escitalopram versus venlafaxine). Most studies had methodological or reporting shortcomings (or both): all studies were at unclear risk of selection and reporting bias. Follow-up rarely extended beyond three months. The lack of adequate power of most of the studies is also a major concern.Few studies explored the effect of SSRIs or SNRIs on migraine frequency, the primary endpoint. Two studies with unclear reporting compared SSRIs and SNRIs to placebo, suggesting a lack of evidence for a difference. Two studies compared SSRIs or SNRIs versus amitriptyline and found no evidence for a difference in terms of migraine frequency (standardised mean difference (SMD) 0.04, 95% confidence interval (CI) -0.72 to 0.80; I(2) = 72%), or other secondary outcomes such as migraine intensity and duration.SSRIs or SNRIs were generally more tolerable than tricyclics. However, the two groups did not differ in terms of the number of participants who withdrew due to adverse advents or for other reasons (one study, odds ratio (OR) 0.39, 95% CI 0.10 to 1.50 and OR 0.42, 95% CI 0.13 to 1.34).We did not find studies comparing SSRIs or SNRIs with pharmacological treatments other than antidepressants (e.g. antiepileptics and anti-hypertensives).
Authors' conclusions: Since the last version of this review, the new included studies have not added high quality evidence to support the use of SSRIs or venlafaxine as preventive drugs for migraine. There is no evidence to consider SSRIs or venlafaxine as more effective than placebo or amitriptyline in reducing migraine frequency, intensity, and duration over two to three months of treatment. No reliable information is available at longer-term follow-up. Our conclusion is that the use of SSRIs and SNRIs for migraine prophylaxis is not supported by evidence.
Conflict of interest statement
RB has no relevant conflicts of interest to declare. CC has no relevant conflicts of interest to declare. CR has no relevant conflicts of interest to declare. DT has no relevant conflicts of interest to declare. RS has no relevant conflicts of interest to declare. LM has no relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures







Update of
-
Selective serotonin re-uptake inhibitors (SSRIs) for preventing migraine and tension-type headaches.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005 Jul 20;(3):CD002919. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002919.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Apr 01;4:CD002919. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002919.pub3. PMID: 16034880 Updated.
References
References to studies included in this review
Adly 1992 {published data only}
-
- Adly C, Straumanis J, Chesson A. Fluoxetine prophylaxis of migraine. Headache 1992;32(2):101‐4. - PubMed
Bank 1994 {published data only}
-
- Bank J. A comparative study of amitriptyline and fluvoxamine in migraine prophylaxis. Headache 1994;34(8):476‐8. - PubMed
Bulut 2004 {published data only}
-
- Bulut S, Berilgen MS, Baran A, Tekatas A, Atmaca M, Mungen B. Venlafaxine versus amitriptyline in the prophylactic treatment of migraine: randomized, double‐blind, crossover study. Clinical Neurology and Neurosurgery 2004;107:44–8. - PubMed
Colucci d'Amato 1999a {published data only}
-
- Colucci d'Amato C, Pizza V, Marmolo T, Giordano E, Alfano V, Nasta A. Fluoxetine for migraine prophylaxis: a double‐blind trial. Headache 1999;39(10):716‐9. - PubMed
Krymchantowski 2002 {published data only}
-
- Krymchantowski AV, Silva MT, Barbosa JS, Alves LA. Amitriptyline versus amitriptyline combined with fluoxetine in the preventative treatment of transformed migraine: a double‐blind study. Headache 2002;42(6):510‐4. - PubMed
Landy 1999 {published data only}
-
- Landy S, McGinnis J, Curlin D, Laizure SC. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors for migraine prophylaxis. Headache 1999;39(1):28‐32. - PubMed
Oguzhanoglu 1999 {published data only}
-
- Oguzhanoglu A, Sahiner T, Kurt T, Akalin O. Use of amitriptyline and fluoxetine in prophylaxis of migraine and tension‐type headaches. Cephalalgia 1999;19(5):531‐2. - PubMed
Ozyalcin 2005 {published data only}
-
- Ozyalcin SN, Talu GK, Kiziltan E, Yucel B, Ertas M, Disci R. The efficacy and safety of venlafaxine in the prophylaxis of migraine. Headache 2005;45(5):144‐52. - PubMed
Polisca 1992 {published data only}
-
- Polisca R, Signoretti P, Marchi P. Fluoxetine in the treatment of migraine with interval headache [La fluoxetina nella terapia della emicrania con cefalea intervallare]. Rassegna Internazionale di Clinica e Terapia 1992;72(9):408‐15.
Steiner 1998 {published data only}
-
- Steiner TJ, Ahmed F, Findley LJ, MacGregor EA, Wilkinson M. S‐fluoxetine in the prophylaxis of migraine: a phase II double‐blind randomized placebo‐controlled study. Cephalalgia 1998;18(5):283‐6. - PubMed
Tarlaci 2009 {published data only}
-
- Tarlaci S. Escitalopram and venlafaxine for the prophylaxis of migraine headache without mood disorders. Clinical Neuropharmacology 2009;32:254‐8. - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Amelin 2000 {published data only}
-
- Amelin AV, Skoromets AA, Korenko LA, Tumelevich BCh, Gonchar MA. A comparative efficiency of amitriptyline, fluoxetine and maprotiline in prevention of migraine in attack‐free period [Sravnitel'naia effektivnost' amitriptilina, fluoksetina i maprotilina pri lechenii migreni v mezhpristupnom periode]. Zhurnal Nevrologii i Psikhiatrii Imeni S.S. Korsakova 2000;100(8):20‐3. - PubMed
Andersson 1981 {published data only}
-
- Andersson PG, Petersen EN. Propranolol and femoxetine, a 5‐HT‐uptake inhibitor, in migraine prophylaxis. A double‐blind crossover study. Acta Neurologica Scandinavica 1981;64(4):280‐8. - PubMed
Bittman 1992 {published data only}
-
- Bittman B, Emanuele S. Fluoxetine: side effects and efficacy in a headache population. Headache Quarterly 1992;3(1):82‐5.
Bussone 1991 {published data only}
-
- Bussone G, Sandrini G, Patruno G, Ruiz L, Tassorelli C, Nappi G. Effectiveness of fluoxetine on pain and depression in chronic headache disorders. In: Nappi G, Bono G, Sandrini G, Martignoni E, Micieli G editor(s). Headache and Depression: Serotonin Pathways as a Common Clue. New York: Raven Press, 1991:265‐72.
Centonze 2000 {published data only}
-
- Centonze V, Bassi A, Cassiano M, Causaran V, Dalfino L, Centonze A, et al. Venlafaxine, serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor for preventive migraine without aura treatment: a preliminary study. Medicina Psicosomatica 2000;45(1):3‐9.
Colucci d'Amato 1998 {published data only}
-
- Colucci d'Amato C, Pizza V, Marmolo T, Giordano E, Alfano V. Paroxetine versus flunarizine in the preventive treatment of migraine. Headache Quarterly 1998;9(3):266‐7.
Colucci d'Amato 1999b {published data only}
-
- Colucci d'Amato C, Pizza V, Marmolo T, Giordano E, Alfano V, Ruggiero A, et al. Experience of treatment with SSRI in migraine prophylaxis [Esperienza del trattamento con SSRI nella profilassi dell'emicrania]. Atti del 14° congresso Nazionale della Societa' Italiana per lo studio delle cefalee; 1999 sett 19‐22; Perugia. 1999:79.
Colucci d'Amato 2000 {published data only}
-
- Colucci d'Amato C, Pizza V, Marmolo T, Giordano E, Alfano V, Ruggiero A. Migraine prophylactic therapy: citalopram versus flunarizine. Headache Quarterly 2000;11(3):213‐5.
Diamond 1989 {published data only}
-
- Diamond S, Freitag FG. The use of fluoxetine in the treatment of headache. Clinical Journal of Pain 1989;5(2):200‐1. - PubMed
Foster 1994 {published data only}
-
- Foster CA, Bafaloukos J. Paroxetine in the treatment of chronic daily headache. Headache 1994;34(10):587‐9. - PubMed
Iannacchero 1999 {published data only}
-
- Iannacchero R, Ambrosio A, Rose F, Flippo A, Ambrosio LA. Efficacy and tolerability of citalopram in chronic headache syndrome prophylaxis [Efficacia e tollerabilita' del citaloprom nella profilassi delle sindromi cefalalgiche cronicizzate: comorbilita' emicrania senz'aura e depressione]. Psichiatria 1999:73‐7.
Kangasniemi 1983 {published data only}
-
- Kangasniemi PJ, Nyrke T, Lang AH, Petersen E. Femoxetine ‐ a new 5‐HT uptake inhibitor ‐ and propranolol in the prophylactic treatment of migraine. Acta Neurologica Scandinavica 1983;68(4):262‐7. - PubMed
Kathpal 1998 {published data only}
-
- Kathpal GS. Role of SSRIs in the management of migraine. Headache Quarterly 1998;9(3):265‐6.
Orholm 1986 {published data only}
-
- Orholm M, Honorè PF, Zeeberg I. A randomized general practice group‐comparative study of femoxetine and placebo in the prophylaxis of migraine. Acta Neurologica Scandinavica 1986;74(3):235‐9. - PubMed
Rampello 2004 {published data only}
-
- Rampello L, Alvano A, Chiechio S, Malaguarnera M, Raffaele R, Vecchio I, et al. Evaluation of the prophylactic efficacy of amitriptyline and citalopram, alone or in combination, in patients with comorbidity of depression, migraine, and tension‐type headache. Neuropsychobiology 2004;50:322‐8. - PubMed
Sandrini 1991 {published data only}
-
- Sandrini G, Ruiz L, Patruno G, Bussone G, Verri AP, Nappi G. Antalgic and antidepressant activities of fluoxetine in daily chronic headache. Cephalalgia 1991;11 Suppl 11:280‐1.
Saper 1994 {published data only}
-
- Saper JR, Silberstein SD, Lake AE 3rd, Winters ME. Double‐blind trial of fluoxetine: chronic daily headache and migraine. Headache 1994;34(9):497‐502. - PubMed
Zeeberg 1981 {published data only}
-
- Zeeberg I, Orholm M, Nielsen JD, Honoré PF, Larsen JJ. Femoxetine in the prophylaxis of migraine ‐ a randomised comparison with placebo. Acta Neurologica Scandinavica 1981;64(6):452‐9. - PubMed
References to studies awaiting assessment
Dzagnidze 2009 {published data only}
-
- Dzagnidze A, Kukava M, Janelidze M, Katsarava M. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor venlafaxine as a prophylactic drug for migraine without aura. European Journal of Neurology 2009;16(3):55–334.
He 2004 {published data only}
-
- He WZ, Chen M, Zheng JZ. Curative effect of fluoxetine for adjuvant treatment of migraine and its effect on serum lipid. Chinese Journal of Clinical Rehabilitation 2004;8(25):5254‐5.
Stanic 2009 {published data only}
-
- Stanic SI, Sretenovic SL. The profilaxis of the frequency of migraine attacks with sertraline and cinarizine. Cephalalgia 2009;29(Suppl 1):142.
Togha 2014 {published data only}
-
- Togha M, Taghdiri F, Razeghi Jahromi S. Efficacy and safety of venlafaxine for the treatment of chronic migraine: a randomized, double‐blind, controlled trial. Journal of Headache and Pain 2014;15(Suppl 1):G38.
References to ongoing studies
NCT01393522 {published data only}
-
- Milnacipran for migraine pain. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01393522 (accessed November 2014).
Additional references
Ad Hoc 1962
-
- Ad Hoc Committee on the Classification of Headache of the National Institute of Neurological Diseases and Blindness. Classification of headache. JAMA 1962;179(9):717‐8.
Altman 1990
-
- Altman DG, Dore CJ. Randomisation and baseline comparisons in clinical trials. Lancet 1990;335(8682):149‐53. - PubMed
American Migraine Foundation 2013
-
- American Migraine Foundation. 36 Million Migraine Campaign. http://www.americanmigrainefoundation.org/support‐the‐foundation/36‐mill... (accessed January 2015).
Bloudek 2012
Buse 2012
-
- Buse D, Manack A, Serrano D, Reed M, Varon S, Turkel C, et al. Headache impact of chronic and episodic migraine: results from the American Migraine Prevalence and Prevention study. Headache 2012;52(1):3‐17. - PubMed
Buse 2013
-
- Buse DC, Silberstein SD, Manack AN, Papapetropoulos S, Lipton RB. Psychiatric comorbidities of episodic and chronic migraine. Journal of Neurology 2013;260(8):1960‐9. - PubMed
Clarke 1996
-
- Clarke CE, MacMillan L, Sondhi S, Wells NEJ. Economic and social impact of migraine. QJM: Monthly Journal of the Association of Physicians 1996;89(1):77‐84. - PubMed
Cohen 1988
-
- Cohen J. Statistical Power Analysis in the Behavioral Sciences. 2nd Edition. Hillsdale (NJ): Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Inc, 1988.
Colas 2004
-
- Colas R, Munoz P, Temprano R, Gomez C, Pascual J. Chronic daily headache with analgesic overuse: epidemiology and impact on quality of life. Neurology 2004;62:1338–42. - PubMed
Cull 1992
-
- Cull RE, Wells NEJ, Miochevic ML. The economic cost of migraine. British Journal of Medical Economics 1992;2:103‐15.
Deeks 2011
-
- Deeks JJ, Higgins JPT, Altman DG (editors). Chapter 9: Analysing data and undertaking meta‐analyses. In: Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Elbourne 2002
-
- Elbourne DR, Altman DG, Higgins JPT, Curtin F, Worthington HV, Vail A. Meta‐analyses involving cross‐over trials: methodological issues. International Journal of Epidemiology 2002;31(1):140‐9. - PubMed
Evers 2009
-
- Evers S, Afra J, Frese A, Goadsby PJ, Linde M, May A, et al. European Federation of Neurological Societies (EFNS) guideline on the drug treatment of migraine – revised report of an EFNS task force. European Journal of Neurology 2009;16(9):968‐81. - PubMed
Guyatt 2008
Hamel 2007
-
- Hamel E. Serotonin and migraine: biology and clinical implications. Cephalalgia 2007;27(11):1293‐300. - PubMed
Higgins 2011
-
- Higgins JPT, Altman DG, Sterne JAC (editors). Chapter 8: Assessing risk of bias in included studies. In: Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Hoffmann 2014
-
- Hoffmann J, Goadsby PJ. Emerging targets in migraine. CNS Drugs 2014;28:11–7. - PubMed
Hotopf 1997
Hotopf 1999
-
- Hotopf M, Churchill R, Lewis G. Pragmatic randomised controlled trials in psychiatry. British Journal of Psychiatry 1999;175:217‐23. - PubMed
Hu 1999
-
- Hu XH, Markson LE, Lipton RB, Stewart WF, Berger ML. Burden of migraine in the United States: disability and economic costs. Archives of Internal Medicine 1999;159(8):813‐8. - PubMed
ICHD‐II 2004
-
- Headache Classification Subcommittee of the International Headache Society. The International Classification of Headache Disorders: 2nd edition. Cephalalgia 2004;24 Suppl(1):1–160. - PubMed
IHS 1988
-
- Headache Classification Committee of the International Headache Society. Classification and diagnostic criteria for headache disorders, cranial neuralgias and facial pain. Cephalalgia 1988;8 Suppl(7):1‐96. - PubMed
IHS 2013
-
- Headache Classification Committee of the International Headache Society (IHS). The International Classification of Headache Disorders, 3rd edition (beta version). Cephalalgia 2013;33(9):629–808. - PubMed
Jackson 2010
Kaniecki 2003
-
- Kaniecki R. Headache assessment and management. JAMA 2003;289(11):1430‐3. - PubMed
Linde 2012
-
- Linde M, Gustavsson A, Stovner LJ, Steiner TJ, Barré J, Katsarava Z, et al. The cost of headache disorders in Europe: the Eurolight project. European Journal of Neurology 2012;19(5):703‐11. - PubMed
Lipton 2001
-
- Lipton RB, Stewart WF, Diamond S, Diamond ML, Reed M. Prevalence and burden of migraine in the United States: data from the American Migraine Study II. Headache 2001;41(7):646‐57. - PubMed
Lipton 2004
-
- Lipton RB, Pan J. Is migraine a progressive brain disease?. JAMA 2004;291:493–4. - PubMed
Lipton 2007
-
- Lipton RB, Bigal ME, Diamond M, Freitag F, Reed ML, Stewart WF, AMPP Advisory Group. Migraine prevalence, disease burden, and the need for preventive therapy. Neurology 2007;68(5):343‐9. - PubMed
Loder 2012
-
- Loder E, Burch R, Rizzoli P. The 2012 AHS/AAN guidelines for prevention of episodic migraine: a summary and comparison with other recent clinical practice guidelines. Headache 2012;52:930‐45. - PubMed
Munakata 2009
-
- Munakata J, Hazard E, Serrano D, Klingman D, Rupnow MF, Tierce J, et al. Economic burden of transformed migraine: results from the American Migraine Prevalence and Prevention (AMPP) Study. Headache 2009;49(4):498‐508. - PubMed
Nappi 1985
-
- Nappi G, Savoldi F. Headache: Diagnostic System and Taxonomic Criteria. London, Paris: J. Libbey Eurotext, 1985.
Natoli 2010
-
- Natoli JL, Manack A, Dean B, Butler Q, Turkel CC, Stovner L, et al. Global prevalence of chronic migraine: a systematic review. Cephalalgia 2010;30(5):599–609. - PubMed
NICE 2012
-
- National Institute of Health and Care Excellence. Headaches: diagnosis and management of headaches in young people and adults. Clinical guidelines, CG150 September 2012:187‐214.
Pocock 1997
-
- Pocock SJ. Clinical trials with multiple outcomes: a statistical perspective on their design, analysis, and interpretation. Controlled Clinical Trials 1997;18(6):530‐45. - PubMed
Pringsheim 2012
-
- Pringsheim T, Davenport WJ, Mackie G, Worthington I, Aubé M, Christie SN, et al. on behalf of the Canadian Headache Society Prophylactic Guidelines Development Group. Canadian Headache Society Guideline for Migraine Prophylaxis. Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences 2012;39 Suppl 2:S1‐S2. - PubMed
RevMan 2014 [Computer program]
-
- The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration. Review Manager (RevMan). Version 5.3. Copenhagen: The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2014.
Serrano 2013
-
- Serrano D, Manack AN, Reed ML, Buse DC, Varon SF, Lipton RB. Cost and predictors of lost productive time in chronic migraine and episodic migraine: results from the American Migraine Prevalence and Prevention (AMPP) Study. Value in Health 2013;16(1):31‐8. - PubMed
Silberstein 1996
-
- Silberstein SD, Lipton RB, Sliwinski M. Classification of daily and near‐daily headaches: field trial of revised IHS criteria. Neurology 1996;47:871‐5. - PubMed
Silberstein 2012
-
- Silberstein SD, Holland S, Freitag F, Dodick DW, Argoff C, Ashman E, Quality Standards Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology and the American Headache Society. Evidence‐based guideline update: pharmacologic treatment for episodic migraine prevention in adults: report of the Quality Standards Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology and the American Headache Society. Neurology 2012;78(17):1337‐45. - PMC - PubMed
Sindrup 2000
-
- Sindrup SH, Jensen TS. Pharmacologic treatment of pain in polyneuropathy. Neurology 2000;55(7):915‐20. - PubMed
Snow 2002
-
- Snow V, Weiss K, Wall EM, Mottur‐Pilson C, for the American Academy of Family Physicians and the American College of Physicians‐American Society of Internal Medicine. Pharmacologic management of acute attacks of migraine and prevention of migraine headache. Annals of Internal Medicine 2002;137(10):840‐9. - PubMed
Sprenger 2009
Steiner 2013
Steward 1992
-
- Stewart WF, Lipton RB, Celentano DD, Reed ML. Prevalence of migraine headache in the United States. Relation to age, income, race, and other sociodemographic factors. JAMA 1992;267(1):64‐9. - PubMed
Tfelt‐Hansen 2012
-
- Tfelt‐Hansen P, Pascual J, Ramadan N, Dahlöf C, D'Amico D, Diener HC, et al. International Headache Society Clinical Trials Subcommittee. Guidelines for controlled trials of drugs in migraine: third edition. A guide for investigators. Cephalalgia 2012;32(1):6‐38. - PubMed
Thornley 1998
Tomkins 2001
-
- Tomkins GE, Jackson JL, O'Malley PG, Balden E, Santoro JE. Treatment of chronic headache with antidepressants: a meta‐analysis. American Journal of Medicine 2001;111(1):54‐63. - PubMed
Von Korff 1998
-
- Korff M, Stewart WF, Simon DJ, Lipton RB. Migraine and reduced work performance: a population‐based study. Neurology 1998;50(6):1741‐5. - PubMed
Vos 2012
Wiendels 2006
-
- Wiendels NJ, Knuistingh Neven A, Rosendaal FR, Spinhoven P, Zitman FG, Assendelft WJ, et al. Chronic frequent headache in the general population: prevalence and associated factors. Cephalalgia 2006;26:1434–42. - PubMed
Williamson 2012
Zwart 2004
-
- Zwart JA, Dyb G, Hagen K, Svebak S, Stovner LJ, Holmen J. Analgesic overuse among subjects with headache, neck, and low‐back pain. Neurology 2004;62(9):1540. - PubMed

