UDP-Sugars as Extracellular Signaling Molecules: Cellular and Physiologic Consequences of P2Y14 Receptor Activation
- PMID: 25829059
- PMCID: PMC4468635
- DOI: 10.1124/mol.115.098756
UDP-Sugars as Extracellular Signaling Molecules: Cellular and Physiologic Consequences of P2Y14 Receptor Activation
Abstract
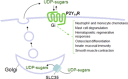
UDP-sugars, which are indispensable for protein glycosylation reactions in cellular secretory pathways, also act as important extracellular signaling molecules. We discuss here the broadly expressed P2Y14 receptor, a G-protein-coupled receptor targeted by UDP sugars, and the increasingly diverse set of physiologic responses discovered recently functioning downstream of this receptor in many epithelia as well as in immune, inflammatory, and other cells.
Copyright © 2015 by The American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics.
Figures


References
-
- Abbracchio MP, Burnstock G, Boeynaems JM, Barnard EA, Boyer JL, Kennedy C, Knight GE, Fumagalli M, Gachet C, Jacobson KA, et al. (2006) International Union of Pharmacology LVIII: update on the P2Y G protein-coupled nucleotide receptors: from molecular mechanisms and pathophysiology to therapy. Pharmacol Rev 58:281–341. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Abeijon C, Hirschberg CB. (1992) Topography of glycosylation reactions in the endoplasmic reticulum. Trends Biochem Sci 17:32–36. - PubMed
-
- Arase T, Uchida H, Kajitani T, Ono M, Tamaki K, Oda H, Nishikawa S, Kagami M, Nagashima T, Masuda H, et al. (2009) The UDP-glucose receptor P2RY14 triggers innate mucosal immunity in the female reproductive tract by inducing IL-8. J Immunol 182:7074–7084. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

