Cbl-b-deficient mice express alterations in trafficking-related molecules but retain sensitivity to the multiple sclerosis therapeutic agent, FTY720
- PMID: 25829233
- PMCID: PMC4420730
- DOI: 10.1016/j.clim.2015.03.018
Cbl-b-deficient mice express alterations in trafficking-related molecules but retain sensitivity to the multiple sclerosis therapeutic agent, FTY720
Abstract
The variable response to therapy in multiple sclerosis (MS) suggests a need for personalized approaches based on individual genetic differences. GWAS have linked CBLB gene polymorphisms with MS and recent evidence demonstrated that these polymorphisms can be associated with abnormalities in T cell function and response to interferon-β therapy. Cbl-b is an E3 ubiquitin ligase that regulates T cell activation and Cbl-b-deficient (Cbl-b(-/-)) mice show T cell abnormalities described in MS patients. We now show that Cbl-b(-/-) T cells demonstrate significant lymph node trafficking abnormalities. We thus asked whether the MS-approved drug, FTY720, postulated to trap T cells in lymphoid tissues, is less effective in the context of Cbl-b dysfunction. We now report that FTY720 significantly inhibits EAE in Cbl-b(-/-) mice. Our results newly document a role for Cbl-b in T cell trafficking but suggest nevertheless that MS patients with Cbl-b abnormalities may still be excellent candidates for FTY720 treatment.
Keywords: Casitas-B lineage lymphoma-b; Experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis; FTY720; Multiple sclerosis; Sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 1; T cell trafficking.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The author (s) declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
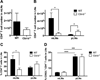
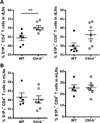
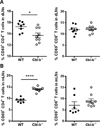
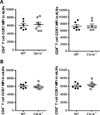

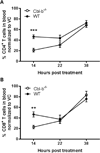
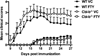
References
-
- International Multiple Sclerosis Genetics, C. Hafler DA, Compston A, Sawcer S, Lander ES, Daly MJ, De Jager PL, de Bakker PI, Gabriel SB, Mirel DB, et al. Risk alleles for multiple sclerosis identified by a genomewide study. N Engl J Med. 2007;357:851–862. - PubMed
-
- International Multiple Sclerosis Genetics, C., C. Wellcome Trust Case Control. Sawcer S, Hellenthal G, Pirinen M, Spencer CC, Patsopoulos NA, Moutsianas L, Dilthey A, Su Z, et al. Genetic risk and a primary role for cell-mediated immune mechanisms in multiple sclerosis. Nature. 2011;476:214–219. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bachmaier K, Krawczyk C, Kozieradzki I, Kong YY, Sasaki T, Oliveira-dos-Santos A, Mariathasan S, Bouchard D, Wakeham A, Itie A, et al. Negative regulation of lymphocyte activation and autoimmunity by the molecular adaptor Cbl-b. Nature. 2000;403:211–216. - PubMed
-
- Chiang YJ, Kole HK, Brown K, Naramura M, Fukuhara S, Hu RJ, Jang IK, Gutkind JS, Shevach E, Gu H. Cbl-b regulates the CD28 dependence of T-cell activation. Nature. 2000;403:216–220. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

