Histology of the heterostracan dermal skeleton: Insight into the origin of the vertebrate mineralised skeleton
- PMID: 25829358
- PMCID: PMC4979667
- DOI: 10.1002/jmor.20370
Histology of the heterostracan dermal skeleton: Insight into the origin of the vertebrate mineralised skeleton
Abstract
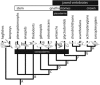
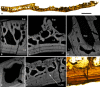
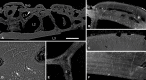
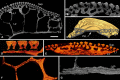
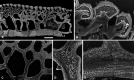
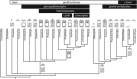
Living vertebrates are divided into those that possess a fully formed and fully mineralised skeleton (gnathostomes) versus those that possess only unmineralised cartilaginous rudiments (cyclostomes). As such, extinct phylogenetic intermediates of these living lineages afford unique insights into the evolutionary assembly of the vertebrate mineralised skeleton and its canonical tissue types. Extinct jawless and jawed fishes assigned to the gnathostome stem evidence the piecemeal assembly of skeletal systems, revealing that the dermal skeleton is the earliest manifestation of a homologous mineralised skeleton. Yet the nature of the primitive dermal skeleton, itself, is poorly understood. This is principally because previous histological studies of early vertebrates lacked a phylogenetic framework required to derive evolutionary hypotheses. Nowhere is this more apparent than within Heterostraci, a diverse clade of primitive jawless vertebrates. To this end, we surveyed the dermal skeletal histology of heterostracans, inferred the plesiomorphic heterostracan skeleton and, through histological comparison to other skeletonising vertebrate clades, deduced the ancestral nature of the vertebrate dermal skeleton. Heterostracans primitively possess a four-layered skeleton, comprising a superficial layer of odontodes composed of dentine and enameloid; a compact layer of acellular parallel-fibred bone containing a network of vascular canals that supply the pulp canals (L1); a trabecular layer consisting of intersecting radial walls composed of acellular parallel-fibred bone, showing osteon-like development (L2); and a basal layer of isopedin (L3). A three layered skeleton, equivalent to the superficial layer L2 and L3 and composed of enameloid, dentine and acellular bone, is possessed by the ancestor of heterostracans + jawed vertebrates. We conclude that an osteogenic component is plesiomorphic with respect to the vertebrate dermal skeleton. Consequently, we interpret the dermal skeleton of denticles in chondrichthyans and jawless thelodonts as independently and secondarily simplified. J. Morphol. 276:657-680, 2015. © 2015 The Authors Journal of Morphology Published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Keywords: bone; dentine; dermoskeleton; enameloid; gnathostome; jawless; microstructure.
© 2015 The Authors Journal of Morphology Published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures


References
-
- Agassiz L. 1835. Recherches sur les Poissons Fossiles. Neuchatel: Petitpierre.
-
- Agassiz L. 1845. Monographie de Poissons Fossiles des Vieux Grès Rouges ou Système Dévonien (Old Red Sandstone) des Îles Britanniques et de Russie. Neuchâtel: Imprimerie de Petitpierre et Prince.
-
- Ball HW, Dineley DL, White E. 1961. The Old Red Sandstone of Brown Clee Hill and the Adjacent Area. London: British Museum (Natural History).
-
- Berg LS. 1940. Classification of Fishes both Recent and Fossil. Trav Inst Zool Acad Sci USSR 5:87–517.
-
- Blieck A. 1984. Les hétérostracés Ptéraspidiformes, agnathes du Silurien‐Dévonien du continent Nord‐Atlantique et des blocs avoisinants: Révision systématique, phylogénie, biostratigraphie, biogéographie. Paris: Centre national de la Recherche Scientifique.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

