Enhanced bactericidal effect of enterocin A in combination with thyme essential oils against L. monocytogenes and E. coli O157:H7
- PMID: 25829595
- PMCID: PMC4375200
- DOI: 10.1007/s13197-013-1214-5
Enhanced bactericidal effect of enterocin A in combination with thyme essential oils against L. monocytogenes and E. coli O157:H7
Abstract
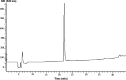
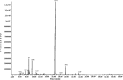
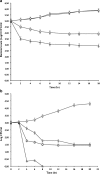
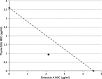
The combined effects of enterocin A with Thymus vulgaris essential oils (EOs) against Listeria monocytogenes and Escherichia coli O157:H7 were investigated in vitro by enumeration of surviving populations of testing pathogens and minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) determination. Enterocin A was purified to homogeneity by RP-HPLC from the culture fluid of Enterococcus strain and thyme EOs were extracted from local Thymus vulgaris plants. The major constituent of thyme EOs oils determined by GC-MS was thymol (78.4 %). Combination of enterocin A with thyme EOs showed an enhanced bactericidal effect against Listeria monocytogenes. Checkerboard assay and isobologram construction displayed a synergistic interaction between these compounds against Listeria (FIC index <0.5). Moreover, the MIC value of enterocin A has fallen fivefold (from 4.57 to 0.9 μg/ml), while the MIC of thyme EOs decreased threefold (from 3.6 to 1.2 μg/ml). Treatments with enterocin A alone did not affect the growth of the enteric pathogen E. coli O157:H7. However, the addition of thyme EOs and enterocin A yielded a synergistic antimicrobial effect against E. coli (MIC thyme EOs decrease from 2.2 to 0.71 μg/ml). This is the first report on the combined effect of enterocin A and thyme EOs against food pathogen bacteria. This combination could be useful in food bio-preservation.
Keywords: Bacteriocins; E. coli; Essential oils; Food preservation; Lactic acid bacteria; Listeria.
Figures
References
-
- Bagamboula CF, Uyttendaele M, Debevere J. Inhibitory effect of thyme and basil essential oils, carvacrol, thymol, estragol, linalool and p-cymene towards Shigella sonnei and S. flexneri. Food Microbiol. 2004;21:33–42. doi: 10.1016/S0740-0020(03)00046-7. - DOI
-
- Bamoniri A, Ebrahimabadi AH, Mazoochi A, Behpour M, Kashi FJ, Batooli H. Antioxidant and antimicrobial activity evaluation and essential oil analysis of Semenovia tragioides Boiss from Iran. Food Chem. 2010;122:553–558. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2010.03.009. - DOI
-
- Borrero J, Kunze G, Jiménez JJ, Böer E, Gútiez L, Herranz C, Cintas LM, Hernández PE. Cloning, production and functional expression of the bacteriocin enterocin A, produced by Enterococcus faecium T136, by the Yeasts Pichia pastoris, Kluyveromyces lactis, Hansenula polymorpha and Arxula adeninivorans. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2012;78:5956–5961. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00530-12. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
