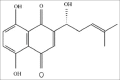
Shikonin induces apoptosis in the human gastric cancer cells HGC-27 through mitochondria-mediated pathway
- PMID: 25829762
- PMCID: PMC4378121
- DOI: 10.4103/0973-1296.153074
Shikonin induces apoptosis in the human gastric cancer cells HGC-27 through mitochondria-mediated pathway
Abstract
Background: Gastric cancer (GC) is one of the most frequently occurring digestive tract cancers and fewer chemotherapeutic drugs for GC have shown promising results. In this study, we investigated the anti-tumor activity of shikonin, a natural compound isolated from the Chinese plant Lithospermum erythrorhizon, against the human GC cell line HGC-27.
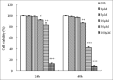
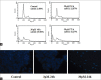
Materials and methods: HGC-27 cells treated with shikonin at a concentration of 30μM or above showed significant growth inhibition compared to control cells. Shikonin-treated cells also underwent apoptosis as detected by flow cytometric analysis and microscopic examination of cellular morphology. Further investigation into the underlying mechanism of apoptosis by western blot showed that the shikonin promoted the activation of poly-(ADP-ribose)-polymerase, caspase-3 and caspase-9 following 24 h or 48 h of treatment time, as well as the activation of caspase-8, but only after 48 h of treatment time. Furthermore, the levels of mitochondrial membrane potential, B-cell lymphoma 2 (Bcl-2) and Bcl-extra large were reduced following shikonin treatment while the level of Bax was increased. In addition, shikonin also caused a significant reduction of the protein Survivin, while having little effect on the expression on X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein.
Conclusion: Taken together, these results showed that the shikonin exhibited its anti-tumor activity against HGC-27 cells through inhibiting cell growth and promoting apoptosis by targeting mitochondrial-related signaling pathway. Our finding may represent a positive step in finding a natural and effective compound that could be important implication for future development of chemotherapeutic and/or chemopreventive agent against GC.
Keywords: Apoptosis; HGC-27 cells; caspases; mitochondrial pathway; shikonin.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
