Comparison of intraoperative brain condition, hemodynamics and postoperative recovery between desflurane and sevoflurane in patients undergoing supratentorial craniotomy
- PMID: 25829905
- PMCID: PMC4374222
- DOI: 10.4103/1658-354X.152866
Comparison of intraoperative brain condition, hemodynamics and postoperative recovery between desflurane and sevoflurane in patients undergoing supratentorial craniotomy
Abstract
Background: Post operative recovery has been reported to be faster with desflurane than sevoflurane anesthesia in previous studies. The use of desflurane is often criticized in neurosurgery due to the concerns of cerebral vasodilation and increase in ICP and studies comparing desflurane and sevoflurane in neurosurgey are scarce. So we compared the intraoperative brain condition, hemodynamics and postoperative recovery in patients undergoing elective supratentorial craniotomy receiving either desflurane or sevoflurane.
Materials and methods: Fifty three patients between 18-60yr undergoing elective supratentorial craniotomy receiving N2O and oxygen (60%:40%) and 0.8-1.2 MAC of either desflurane or sevoflurane were randomized to group S (Sevoflurane) or group D (Desflurane). Subdural intra cranial pressure (ICP) was measured and brain condition was assessed.. Emergence time, tracheal extubation time and recovery time were recorded. Cognitive behavior was evaluated with Short Orientation Memory Concentration Test (SOMCT) and neurological outcome (at the time of discharge) was assessed using Glasgow Outcome Score (GOS) between the two groups.
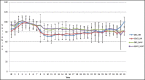
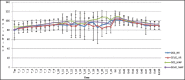
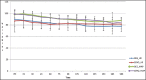
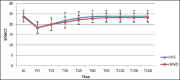
Results: The emergence time [Group D 7.4 ± 2.7 minutes vs. Group S 7.8 ± 3.7 minutes; P = 0.65], extubation time [Group D 11.8 ± 2.8 minutes vs. Group S 12.9 ± 4.9 minutes; P = 0.28] and recovery time [Group D 16.4 ± 2.6 minutes vs. Group S 17.1 ± 4.8 minutes; P = 0.50] were comparable between the two groups. There was no difference in ICP [Group D; 9.1 ± 4.3 mmHg vs. Group S; 10.9 ± 4.2 mmHg; P = 0.14] and brain condition between the two groups. Both groups had similar post-operative complications, hospital and ICU stay and GOS.
Conclusion: In patients undergoing elective supratentorial craniotomy both sevoflurane and desflurane had similar intra-operative brain condition, hemodynamics and post operative recovery profile.
Keywords: Desflurane; intracranial pressure; recovery; sevoflurane; supratentorial craniotomy.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Heavner JE, Kaye AD, Lin BK, King T. Recovery of elderly patients from two or more hours of desflurane or sevoflurane anesthesia. Br J Anesth. 2003;91:502–6. - PubMed
-
- Lutz LJ, Milde JH, Milde LN. The response of the canine cerebral circulation to hyperventilation during anesthesia with desflurane. Anesthesiology. 1991;74:504–7. - PubMed
-
- Milde LN, Milde JH. The cerebral and systemic hemodynamic and metabolic effects of desflurane-induced hypotension in dogs. Anesthesiology. 1991;74:513–8. - PubMed
-
- Muzzi DA, Losasso TJ, Dietz NM, Faust RJ, Cucchiara RF, Milde LN. The effect of desflurane and isoflurane on cerebrospinal fluid pressure in humans with supratentorial mass lesions. Anesthesiology. 1992;76:720–4. - PubMed
-
- Magni G, Rosa IL, Melillo G, Savio A, Rosa G. A comparison between sevoflurane and desflurane anesthesia in patients undergoing craniotomy for supratentorial intracranial surgery. Anesth Analg. 2009;109:567–71. - PubMed

