Ganoderma Lucidum Pharmacopuncture for Teating Ethanol-induced Chronic Gastric Ulcers in Rats
- PMID: 25830061
- PMCID: PMC4379478
- DOI: 10.3831/KPI.2015.18.008
Ganoderma Lucidum Pharmacopuncture for Teating Ethanol-induced Chronic Gastric Ulcers in Rats
Abstract
Objectives: The stomach is a sensitive digestive organ that is susceptible to exogenous pathogens from the diet. In response to such pathogens, the stomach induces oxidative stress, which might be related to the development of both gastric organic disorders such as gastritis, gastric ulcers, and gastric cancer, and functional disorders such as functional dyspepsia. This study was accomplished to investigate the effect of Ganoderma lucidum pharmacopuncture (GLP) on chronic gastric ulcers in rats.
Methods: The rats were divided into 4 groups of 8 animals each: the normal, the control, the normal saline (NP) and the GLP groups. In this study, the modified ethanol gastritis model was used. The rats were administrated 56% ethanol orally every other day. The dose of ethanol was 8 g/kg body weight. The normal group received the same amount of normal saline instead of ethanol. The NP and the GLP groups were treated with injection of saline and GLP respectively. The control group received no treatment. Two local acupoints CV12 () and ST36 () were used. All laboratory rats underwent treatment for 15 days. On last day, the rats were sacrificed and their stomachs were immediately excised.
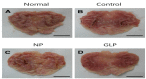
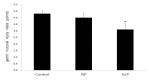
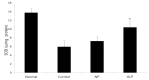
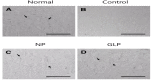
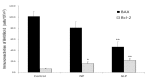
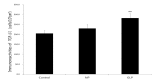
Results: Ulcers of the gastric mucosa appeared as elongated bands of hemorrhagic lesions parallel to the long axis of the stomach. In the NP and GLP groups, the injuries to the gastric mucosal injuries were not as severe as they were in the control group. Wound healings of the chronic gastric ulcers was promoted by using GLP and significant alterations of the indices in the gastric mucosa were observed. Such protection was demonstrated by gross appearance, histology and immunehistochemistry staining for Bcl-2-associated X (BAX), B-cell lymphoma 2 (Bcl-2) and Transforming growth factor-beta 1 (TGF-β1).
Conclusion: These results suggest that GLP at CV12 and ST36 can provide significant protection to the gastric mucosa against an ethanol induced chronic gastric ulcer.
Keywords: Ganoderma lucidum; chronic gastric ulcer; ethanol induced; functional dyspepsia; gastric mucosa; pharmacopuncture.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



Similar articles
-
Ganoderma lucidum Pharmacopuncture for the Treatment of Acute Gastric Ulcers in Rats.J Pharmacopuncture. 2014 Sep;17(3):40-9. doi: 10.3831/KPI.2014.17.025. J Pharmacopuncture. 2014. PMID: 25780708 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatoprotective Evaluation of Ganoderma lucidum Pharmacopuncture: In vivo Studies of Ethanol-induced Acute Liver Injury.J Pharmacopuncture. 2014 Sep;17(3):16-24. doi: 10.3831/KPI.2014.17.022. J Pharmacopuncture. 2014. PMID: 25780705 Free PMC article.
-
Glucagon-like peptide-2 protects the gastric mucosa via regulating blood flow and metabolites.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Dec 16;13:1036559. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.1036559. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36589839 Free PMC article.
-
Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharide fractions accelerate healing of acetic acid-induced ulcers in rats.J Med Food. 2004 Winter;7(4):417-21. doi: 10.1089/jmf.2004.7.417. J Med Food. 2004. PMID: 15671683
-
Protective effects of Ginkgo biloba extract on the ethanol-induced gastric ulcer in rats.World J Gastroenterol. 2005 Jun 28;11(24):3746-50. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i24.3746. World J Gastroenterol. 2005. PMID: 15968732 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Gastroprotective effect of carob (Ceratonia siliqua L.) against ethanol-induced oxidative stress in rat.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2015 Aug 20;15:292. doi: 10.1186/s12906-015-0819-9. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2015. PMID: 26289579 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Elaeagnus angustifolia Honey in the Protection Against Ethanol-Induced Chronic Gastric Injury via Counteracting Oxidative Stress, Interfering with Inflammation and Regulating Gut Microbiota in Mice.Foods. 2025 May 1;14(9):1600. doi: 10.3390/foods14091600. Foods. 2025. PMID: 40361682 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Ganoderic Acid A on Gastrointestinal Motility and Brain-Gut Peptide in Rats with Functional Dyspepsia.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022 May 31;2022:2298665. doi: 10.1155/2022/2298665. eCollection 2022. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022. Retraction in: Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2023 Oct 4;2023:9753670. doi: 10.1155/2023/9753670. PMID: 35685728 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Protective effects of orange (Citrus sinensis L.) peel aqueous extract and hesperidin on oxidative stress and peptic ulcer induced by alcohol in rat.Lipids Health Dis. 2017 Aug 14;16(1):152. doi: 10.1186/s12944-017-0546-y. Lipids Health Dis. 2017. PMID: 28806973 Free PMC article.
-
Diospyros kaki fruit aqueous extract individual/combined with famotidine mitigates peptic ulcer induced by alcohol in rats.Toxicol Res (Camb). 2024 Sep 27;13(5):tfae155. doi: 10.1093/toxres/tfae155. eCollection 2024 Oct. Toxicol Res (Camb). 2024. PMID: 39345794
References
-
- Naito Y, Yoshikawa T. Molecular and cellular mechanisms involved in helicobacter pylori-induced inflammation and oxidative stress. Free Radic Biol Med. 2002;33(3):323–336. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
