Safety management practices in small and medium enterprises in India
- PMID: 25830070
- PMCID: PMC4371889
- DOI: 10.1016/j.shaw.2014.10.006
Safety management practices in small and medium enterprises in India
Abstract
Background: Small and medium enterprises (SMEs) are often the main pillar of an economy. Minor accidents, ergonomics problems, old and outdated machinery, and lack of awareness have created a need for implementation of safety practices in SMEs. Implementation of healthy working conditions creates positive impacts on economic and social development.
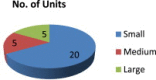
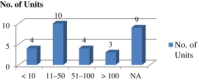
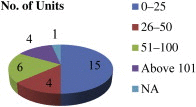
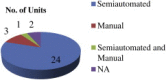
Methods: In this study, a questionnaire was developed and administered to 30 randomly chosen SMEs in and around Mumbai, Maharashtra, and other states in India to evaluate safety practices implemented in their facilities. The study also looked into the barriers and drivers for technology innovation and suggestions were also received from the respondent SMEs for best practices on safety issues.
Results: In some SMEs, risks associated with safety issues were increased whereas risks were decreased in others. Safety management practices are inadequate in most SMEs. Market competitiveness, better efficiency, less risk, and stringent laws were found to be most significant drivers; and financial constraints, lack of awareness, resistance to change, and lack of training for employees were found to be main barriers.
Conclusion: Competition between SMEs was found to be major reason for implementation of safety practices in the SMEs. The major contribution of the study has been awareness building on safety issues in the SMEs that participated in the project.
Keywords: best practices; safety; small and medium sized enterprises.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Financial Budgets of Technology-Based SMEs From the Perspective of Sustainability and Big Data.Front Public Health. 2022 May 4;10:861074. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.861074. eCollection 2022. Front Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35602131 Free PMC article.
-
Assessing the mechanism of barriers towards green finance and public spending in small and medium enterprises from developed countries.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2021 Nov;28(43):60495-60510. doi: 10.1007/s11356-021-14907-1. Epub 2021 Jun 22. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2021. PMID: 34156623
-
Barriers to adaptation of environmental sustainability in SMEs: A qualitative study.PLoS One. 2024 May 16;19(5):e0298580. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0298580. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38753854 Free PMC article.
-
Proposing Circular Economy Ecosystem for Chinese SMEs: A Systematic Review.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021 Mar 1;18(5):2395. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18052395. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021. PMID: 33804522 Free PMC article.
-
Mapping ergonomics application to improve SMEs working condition in industrially developing countries: a critical review.Ergonomics. 2014;57(12):1771-94. doi: 10.1080/00140139.2014.953213. Epub 2014 Sep 12. Ergonomics. 2014. PMID: 25216158 Review.
Cited by
-
Reducing Waste in Healthcare through Occupational Safety and Health Measures: A Study of Manufacturing Industries in Taiwan.Healthcare (Basel). 2021 Oct 30;9(11):1476. doi: 10.3390/healthcare9111476. Healthcare (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34828522 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Berry A. ITD Global Conference on Taxation of Small and Medium Enterprises; Argentina: 2007. The importance of SMEs in the economy.
-
- Keskìn H., Sentürk C., Sungur O., Kìrìs H.M. Bosnia and Herzegovina; Sarajevo: 2010. The importance of SMEs in developing economies. 2nd International Symposium on Sustainable Development.
-
- Europe–India SME Business Council [Internet] 2014. Definition of Indian SMEs.http://www.eisbc.org/Definition_of_Indian_SMEs.aspx [cited 2014 April 17] Available from:
-
- Ministry of Micro Small and Medium Enterprises of India. (a) Growth and performance of MSMEs and (b) 4th Census of MSMEs. Annual Report, 2010–2011; Chapter II: pp. 11–26.
-
- Ministry of Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises, Govt. of India. Growth and performance of MSME sector and (b) Census. Annual Report, 2012–2013; Chapter II: pp. 11–36.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources