Chronic hyperglycemia downregulates GLP-1 receptor signaling in pancreatic β-cells via protein kinase A
- PMID: 25830090
- PMCID: PMC4354925
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molmet.2015.01.010
Chronic hyperglycemia downregulates GLP-1 receptor signaling in pancreatic β-cells via protein kinase A
Abstract
Objective: Glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) enhances insulin secretion and protects β-cell mass. Diabetes therapies targeting the GLP-1 receptor (GLP-1R), expressed in numerous tissues, have diminished dose-response in patients with type 2 diabetes compared with healthy human controls. The aim of this study was to determine the mechanistic causes underlying the reduced efficacy of GLP-1R ligands.
Methods: Using primary mouse islets and the β-cell line MIN6, outcomes downstream of the GLP-1R were analyzed: Insulin secretion; phosphorylation of the cAMP-response element binding protein (CREB); cAMP responses. Signaling systems were studied by immunoblotting and qRT-PCR, and PKA activity was assayed. Cell surface localization of the GLP-1R was studied by confocal microscopy using a fluorescein-tagged exendin-4 and GFP-tagged GLP-1R.
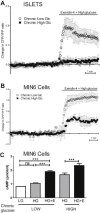
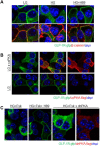
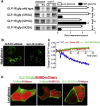
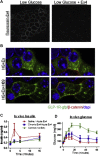
Results: Rodent β-cells chronically exposed to high glucose had diminished responses to GLP-1R agonists including: diminished insulin secretory response; reduced phosphorylation of (CREB); impaired cAMP response, attributable to chronically increased cAMP levels. GLP-1R signaling systems were affected by hyperglycemia with increased expression of mRNAs encoding the inducible cAMP early repressor (ICER) and adenylyl cyclase 8, reduced PKA activity due to increased expression of the PKA-RIα subunit, reduced GLP-1R mRNA expression and loss of GLP-1R from the cell surface. To specifically examine the loss of GLP-1R from the plasma membrane a GLP-1R-GFP fusion protein was employed to visualize subcellular localization. Under low glucose conditions or when PKA activity was inhibited, GLP-1R-GFP was found at the plasma membrane. Conversely high glucose, expression of a constitutively active PKA subunit, or exposure to exendin-4 or forskolin led to GLP-1R-GFP internalization. Mutation of serine residue 301 of the GLP-1R abolished the glucose-dependent loss of the receptor from the plasma membrane. This was associated with a loss of an interaction between the receptor and the small ubiquitin-related modifier (SUMO), an interaction that was found to be necessary for internalization of the receptor.
Conclusions: These data show that glucose acting, at least in part, via PKA leads to the loss of the GLP-1R from the cell surface and an impairment of GLP-1R signaling, which may underlie the reduced clinical efficacy of GLP-1R based therapies in individuals with poorly controlled hyperglycemia.
Keywords: GLP-1 receptor; Hyperglycemia; Protein kinase A; Small ubiquitin-related modifier.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Obestatin promotes survival of pancreatic beta-cells and human islets and induces expression of genes involved in the regulation of beta-cell mass and function.Diabetes. 2008 Apr;57(4):967-79. doi: 10.2337/db07-1104. Epub 2007 Dec 27. Diabetes. 2008. PMID: 18162507
-
SUMO downregulates GLP-1-stimulated cAMP generation and insulin secretion.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2012 Mar 15;302(6):E714-23. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00486.2011. Epub 2012 Jan 10. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2012. PMID: 22234371 Free PMC article.
-
The peptide-hormone glucagon-like peptide-1 activates cAMP and inhibits growth of breast cancer cells.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2012 Apr;132(2):449-61. doi: 10.1007/s10549-011-1585-0. Epub 2011 Jun 3. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2012. PMID: 21638053
-
GLP-1R in diabetes mellitus: from basic discovery to therapeutics development.Front Pharmacol. 2025 May 30;16:1610512. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1610512. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40520185 Free PMC article. Review.
-
GLP-1 based therapeutics: simultaneously combating T2DM and obesity.Front Neurosci. 2015 Mar 20;9:92. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2015.00092. eCollection 2015. Front Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 25852463 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Accumulation of 3-hydroxytetradecenoic acid: Cause or corollary of glucolipotoxic impairment of pancreatic β-cell bioenergetics?Mol Metab. 2015 Oct 8;4(12):926-39. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2015.09.010. eCollection 2015 Dec. Mol Metab. 2015. PMID: 26909309 Free PMC article.
-
Is it safe to acutely discontinue insulin therapy in patients with chronic hyperglycaemia starting GLP-1R agonists?BMJ Case Rep. 2017 Jul 14;2017:bcr2017220437. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2017-220437. BMJ Case Rep. 2017. PMID: 28710307 Free PMC article.
-
The past, present, and future physiology and pharmacology of glucagon.Cell Metab. 2022 Nov 1;34(11):1654-1674. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2022.10.001. Cell Metab. 2022. PMID: 36323234 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In situ graphene liquid cell-transmission electron microscopy study of insulin secretion in pancreatic islet cells.Int J Nanomedicine. 2019 Jan 7;14:371-382. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S169506. eCollection 2019. Int J Nanomedicine. 2019. PMID: 30662261 Free PMC article.
-
β-Cell Knockout of SENP1 Reduces Responses to Incretins and Worsens Oral Glucose Tolerance in High-Fat Diet-Fed Mice.Diabetes. 2021 Nov;70(11):2626-2638. doi: 10.2337/db20-1235. Epub 2021 Aug 30. Diabetes. 2021. PMID: 34462260 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Drucker D.J., Nauck M.A. The incretin system: glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists and dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors in type 2 diabetes. Lancet. 2006;368(9548):1696–1705. - PubMed
-
- Furman B., Pyne N., Flatt P., O'Harte F. Targeting beta-cell cyclic 3'5' adenosine monophosphate for the development of novel drugs for treating type 2 diabetes mellitus. A review. The Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology. 2004;56(12):1477–1492. - PubMed
-
- Zander M., Madsbad S., Madsen J.L., Holst J.J. Effect of 6-week course of glucagon-like peptide 1 on glycaemic control, insulin sensitivity, and beta-cell function in type 2 diabetes: a parallel-group study. Lancet. 2002;359(9309):824–830. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

