Left ventricular diastolic function and dysfunction: Central role of echocardiography
- PMID: 25830147
- PMCID: PMC4374097
- DOI: 10.5339/gcsp.2015.3
Left ventricular diastolic function and dysfunction: Central role of echocardiography
Abstract
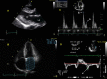
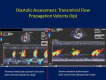
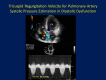
Comprehensive and precise assessment of left ventricular (LV) systolic and diastolic function is necessary to establish, or exclude, heart failure as a cause or component of dyspnea. Echocardiography with Doppler readily assesses LV diastolic function; advantages include that echocardiography is non-invasive, does not require radiation, is portable, rapid, readily available, and in competent hands, can provide an accurate and comprehensive assessment of LV systolic and diastolic function. Correct assessment of LV diastolic function is relevant in patients with both depressed and preserved LV ejection fraction (EF ≥ 50%, and < 50%, respectively). Tissue Doppler (TD) imaging has been useful in demonstrating impaired LV relaxation in the setting of preserved LVEF, which, in the setting of increased cardiac volume, can result in elevated LV filling pressures, and dyspnea due to diastolic heart failure. TD imaging is not always critical in patients with depressed LVEF, since such patients by definition have impaired LV relaxation, and thus significant increases in volume will result in increases in LV filling pressure due to impaired LV compliance. Thus, in depressed LVEF, transmitral flow velocities (E and A, and E/A) and deceleration time, pulmonary venous Doppler, left atrial volume, and pulmonary artery (PA) pressures suffice for the accurate assessment of LV filling pressures. Overall, diastolic assessment by echo-Doppler can be readily achieved in by using a comprehensive diastolic assessment-incorporating many 2-dimensional, conventional and tissue Doppler variables-as opposed to relying on any single, diastolic parameter, which can lead to errors.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Clinical aspects of left ventricular diastolic function assessed by Doppler echocardiography following acute myocardial infarction.Dan Med Bull. 2001 Nov;48(4):199-210. Dan Med Bull. 2001. PMID: 11767125 Review.
-
[Diastolic function of the left ventricle and congestive heart failure with normal systolic function].Ital Heart J Suppl. 2000 Oct;1(10):1273-80. Ital Heart J Suppl. 2000. PMID: 11068708 Review. Italian.
-
[Evaluation of left ventricular diastolic function using Doppler echocardiography].Med Pregl. 1999 Jan-Feb;52(1-2):13-8. Med Pregl. 1999. PMID: 10352498 Review. Croatian.
-
Left ventricular filling hemodynamics in patients with pulmonary edema and preserved versus reduced left ventricular ejection fraction: a prospective Doppler echocardiographic study.J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2006 Jun;19(6):733-43. doi: 10.1016/j.echo.2005.10.019. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2006. PMID: 16762750 Clinical Trial.
-
Left atrial strain: a new parameter for assessment of left ventricular filling pressure.Heart Fail Rev. 2016 Jan;21(1):65-76. doi: 10.1007/s10741-015-9520-9. Heart Fail Rev. 2016. PMID: 26687372 Review.
Cited by
-
Pulmonary vascular disease in the setting of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction.Trends Cardiovasc Med. 2019 May;29(4):207-217. doi: 10.1016/j.tcm.2018.08.005. Epub 2018 Aug 17. Trends Cardiovasc Med. 2019. PMID: 30177249 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interrelations of aortic spring function, cardiovascular disease risk factors, and left ventricular diastolic function: The Framingham Heart Study.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Jul 1:2025.06.30.25330569. doi: 10.1101/2025.06.30.25330569. medRxiv. 2025. PMID: 40630593 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Echocardiographic Abnormalities in Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease (ADPKD) Patients.J Clin Med. 2022 Oct 11;11(20):5982. doi: 10.3390/jcm11205982. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 36294302 Free PMC article.
-
Echocardiography E/A Abnormality is Associated with the Development of Primary Left Ventricle Remodeling in Middle-Aged and Elderly Women: A Longitudinal Study.Clin Interv Aging. 2023 Apr 18;18:629-638. doi: 10.2147/CIA.S399996. eCollection 2023. Clin Interv Aging. 2023. PMID: 37096218 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative analysis of the addition of empagliflozin versus doubling the furosemide dose in decompensated heart failure.Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2024 Jun 12. doi: 10.1007/s10557-024-07593-x. Online ahead of print. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2024. PMID: 38864970
References
-
- Paulus WJ, Tschöpe C, Sanderson JE, Rusconi C, Flachskampf FA, Rademakers FE, Marino P, Smiseth OA, De Keulenaer G, Leite-Moreira AF, Borbély A, Edes I, Handoko ML, Heymans S, Pezzali N, Pieske B, Dickstein K, Fraser AG, Brutsaert DL. How to diagnose diastolic heart failure: a consensus statement on the diagnosis of heart failure with normal left ventricular ejection fraction by the Heart Failure and Echocardiography Associations of the European Society of Cardiology. Eur Heart J. 2007;28:2539–2550. - PubMed
-
- Zile MR, Baicu CF, Gaasch WH. Diastolic heart failure – abnormalities in active relaxation and passive stiffness of the left ventricle. N Engl J Med. 2004;350:1953–1959. - PubMed
-
- Oh JK, Hatle L, Tajik AJ, Little WC. Diastolic heart failure can be diagnosed by comprehensive two-dimensional and Doppler echocardiography. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2006;47:500–506. - PubMed
-
- Lester SJ, Tajik AJ, Nishimura RA, Oh JK, Khandheria BK, Seward JB. Unlocking the mysteries of diastolic function: deciphering the Rosetta Stone 10 years later. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2008;51:679–689. - PubMed
-
- Nagueh SF, Appleton CP, Gillebert TC, Marino PN, Oh JK, Smiseth OA, Waggoner AD, Flachskampf FA, Pellikka PA, Evangelista A. Recommendations for the Evaluation of Left Ventricular Diastolic Function by Echocardiography. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2009;22:107–133. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
