Effects of lifestyle interventions that include a physical activity component in class II and III obese individuals: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 25830342
- PMCID: PMC4382170
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0119017
Effects of lifestyle interventions that include a physical activity component in class II and III obese individuals: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: In class II and III obese individuals, lifestyle intervention is the first step to achieve weight loss and treat obesity-related comorbidities before considering bariatric surgery. A systematic review, meta-analysis, and meta-regression were performed to assess the impact of lifestyle interventions incorporating a physical activity (PA) component on health outcomes of class II and III obese individuals.
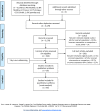
Methods: An electronic search was conducted in 4 databases (Medline, Scopus, CINAHL and Sportdiscus). Two independent investigators selected original studies assessing the impact of lifestyle interventions with PA components on anthropometric parameters, cardiometabolic risk factors (fat mass, blood pressure, lipid and glucose metabolism), behaviour modification (PA and nutritional changes), and quality of life in adults with body mass index (BMI) ≥ 35 kg/m2. Estimates were pooled using a random-effect model (DerSimonian and Laird method). Heterogeneity between studies was assessed by the Cochran's chi-square test and quantified through an estimation of the I².
Results: Of the 3,170 identified articles, 56 met our eligibility criteria, with a large majority of uncontrolled studies (80%). The meta-analysis based on uncontrolled studies showed significant heterogeneity among all included studies. The pooled mean difference in weight loss was 8.9 kg (95% CI, 10.2-7.7; p < 0.01) and 2.8 kg/m² in BMI loss (95% CI, 3.4-2.2; p < 0.01). Long-term interventions produced superior weight loss (11.3 kg) compared to short-term (7.2 kg) and intermediate-term (8.0 kg) interventions. A significant global effect of lifestyle intervention on fat mass, waist circumference, blood pressure, total cholesterol, LDL-C, triglycerides and fasting insulin was found (p<0.01), without significant effect on HDL-C and fasting blood glucose.
Conclusions: Lifestyle interventions incorporating a PA component can improve weight and various cardiometabolic risk factors in class II and III obese individuals. However, further high quality trials are needed to confirm this evidence, especially beyond weight loss.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- World Health Organisation (2014) Obesity and overweight. Fact sheet N°311. Available: http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs311/en/. Accessed 19 August 2014.
-
- Shields M, Carroll MD, Ogden CL. Adult obesity prevalence in Canada and the United States NCHS Data Brief; 2011: 1–8. - PubMed
-
- Bray GA. Medical consequences of obesity. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2004;89: 2583–2589. - PubMed
-
- Must A, Spadano J, Coakley EH, Field AE, Colditz G, Dietz WH. The disease burden associated with overweight and obesity. JAMA. 1999;282: 1523–1529. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

