Involvement of GluR2 up-regulation in neuroprotection by electroacupuncture pretreatment via cannabinoid CB1 receptor in mice
- PMID: 25830356
- PMCID: PMC4381620
- DOI: 10.1038/srep09490
Involvement of GluR2 up-regulation in neuroprotection by electroacupuncture pretreatment via cannabinoid CB1 receptor in mice
Abstract
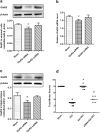
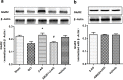
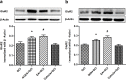
We investigated whether glutamate receptor subunit 2 (GluR2) is involved in EA pretreatment-induced neuroprotection via cannabinoid CB1 receptors (CB1R) after global cerebral ischemia in mice. Two hours after electric acupuncture (EA) pretreatment, global cerebral ischemia (GCI) was induced by bilateral common carotid artery occlusion (BCCAO) for 20 min. The GluR2 expression was examined in the hippocampus after reperfusion. Cell survival, neuronal apoptosis, the Bax/Bcl-2 ratio and neurological scores were evaluated at 24 h after BCCAO in the presence or absence of the GluR2 inhibitor. Furthermore, the GluR2 was determined in the presence and absence of CB1R inhibitor. Our results showed EA pretreatment enhanced expression of GluR2 in the hippocampus 2 h after reperfusion. Moreover, EA pretreatment improved neurological outcome, promoted cell survival, inhibited neuronal apoptosis, and decreased the Bax/Bcl-2 ratio after reperfusion. GluR2 knockdown by GluR2 siRNA effectively reversed the beneficial effects of EA pretreatment. Furthermore, CB1R siRNA and two CB1R antagonists blocked the elevation of GluR2 expression by EA pretreatment, whereas the two CB1R agonists up-regulated GluR2 expression as EA pretreatment. In conclusion, GluR2 up-regulation is involved in neuroprotection of EA pretreatment against GCI through CB1R, suggesting that GluR2 may be a novel target for stroke intervention.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Activation of STAT3 is involved in neuroprotection by electroacupuncture pretreatment via cannabinoid CB1 receptors in rats.Brain Res. 2013 Sep 5;1529:154-64. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2013.07.006. Epub 2013 Jul 20. Brain Res. 2013. PMID: 23880371
-
Mn-SOD Upregulation by Electroacupuncture Attenuates Ischemic Oxidative Damage via CB1R-Mediated STAT3 Phosphorylation.Mol Neurobiol. 2016 Jan;53(1):331-343. doi: 10.1007/s12035-014-8971-7. Epub 2014 Nov 29. Mol Neurobiol. 2016. PMID: 25432886
-
Pretreatment with electroacupuncture induces rapid tolerance to focal cerebral ischemia through regulation of endocannabinoid system.Stroke. 2009 Jun;40(6):2157-64. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.108.541490. Epub 2009 Apr 16. Stroke. 2009. PMID: 19372445
-
Stimulated CB1 Cannabinoid Receptor Inducing Ischemic Tolerance and Protecting Neuron from Cerebral Ischemia.Cent Nerv Syst Agents Med Chem. 2017;17(2):141-150. doi: 10.2174/1871524916666160504104624. Cent Nerv Syst Agents Med Chem. 2017. PMID: 27142423 Review.
-
Electroacupuncture Pretreatment as a Novel Avenue to Protect Heart against Ischemia and Reperfusion Injury.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020 May 18;2020:9786482. doi: 10.1155/2020/9786482. eCollection 2020. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020. PMID: 32508960 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Electro-acupuncture Pretreatment at Zusanli (ST36) Acupoint Attenuates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammation in Rats by Inhibiting Ca2+ Influx Associated with Cannabinoid CB2 Receptors.Inflammation. 2019 Feb;42(1):211-220. doi: 10.1007/s10753-018-0885-5. Inflammation. 2019. PMID: 30168040
-
The effects of acupuncture on psychological symptoms in patients with insomnia: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial.Trials. 2022 Feb 15;23(1):152. doi: 10.1186/s13063-022-06078-2. Trials. 2022. PMID: 35168637 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms Involved in the Neuroprotection of Electroacupuncture Therapy for Ischemic Stroke.Front Neurosci. 2018 Dec 11;12:929. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2018.00929. eCollection 2018. Front Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 30618558 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Possible Effects of Acupuncture in Poststroke Aphasia.Behav Neurol. 2023 Apr 12;2023:9445381. doi: 10.1155/2023/9445381. eCollection 2023. Behav Neurol. 2023. PMID: 37091130 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Combination of stem cell therapy and acupuncture to treat ischemic stroke: a prospective review.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022 Mar 3;13(1):87. doi: 10.1186/s13287-022-02761-y. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022. PMID: 35241146 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hoyert D. L. & Xu J. Deaths: preliminary data for 2011. Natl Vital Stat Rep. 61, 1–51 (2012). - PubMed
-
- Choi D. W. Calcium: still center-stage in hypoxic-ischemic neuronal death. Trends Neurosci. 18, 58–60 (1995). - PubMed
-
- Kwak S. & Weiss J. H. Calcium-permeable AMPA channels in neurodegenerative disease and ischemia. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 16, 281–287 (2006). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

