Pathway as a pharmacological target for herbal medicines: an investigation from reduning injection
- PMID: 25830385
- PMCID: PMC4382287
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0123109
Pathway as a pharmacological target for herbal medicines: an investigation from reduning injection
Abstract
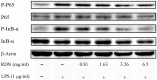
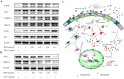
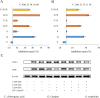
As a rich natural resource for drug discovery, Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) plays an important role in complementary and alternative medical systems. TCM shows a daunting complexity of compounds featuring multi-components and multi-targets to cure diseases, which thus always makes it extremely difficult to systematically explain the molecular mechanisms adequately using routine methods. In the present work, to reveal the systematic mechanism of herbal formulae, we developed a pathway-based strategy by combining the pathways integrating, target selection, reverse drug targeting and network analysis together, and then exemplified it by Reduning injection (RDN), a clinically widely used herbal medicine injection, in combating inflammation. The anti-inflammatory effects exerted by the major ingredients of RDN at signaling pathways level were systematically investigated. More importantly, our predicted results were also experimentally validated. Our strategy provides a deep understanding of the pharmacological functions of herbal formulae from molecular to systematic level, which may lead to more successful applications of systems pharmacology for drug discovery and development.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

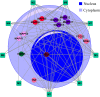
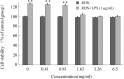
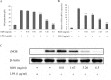
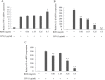
Similar articles
-
Insight into the molecular mechanism of a herbal injection by integrating network pharmacology and in vitro.J Ethnopharmacol. 2015 Sep 15;173:91-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2015.07.016. Epub 2015 Jul 17. J Ethnopharmacol. 2015. PMID: 26192807
-
Revealing active ingredients, potential targets, and action mechanism of Ermiao fang for treating endometritis based on network pharmacology strategy.J Ethnopharmacol. 2020 Oct 5;260:113051. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2020.113051. Epub 2020 Jun 4. J Ethnopharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32505843
-
Network pharmacology study on the mechanism of traditional Chinese medicine for upper respiratory tract infection.Mol Biosyst. 2014 Oct;10(10):2517-25. doi: 10.1039/c4mb00164h. Mol Biosyst. 2014. PMID: 25000319
-
Traditional Chinese medicine network pharmacology: theory, methodology and application.Chin J Nat Med. 2013 Mar;11(2):110-20. doi: 10.1016/S1875-5364(13)60037-0. Chin J Nat Med. 2013. PMID: 23787177 Review.
-
Naturally derived anti-inflammatory compounds from Chinese medicinal plants.J Ethnopharmacol. 2013 Mar 7;146(1):9-39. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2012.12.013. Epub 2012 Dec 26. J Ethnopharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23274744 Review.
Cited by
-
The synergistic Reduning and cefmetazole sodium treatment of severe pneumonia is mediated by the AhR-Src-STAT3 pathway.J Thorac Dis. 2022 Feb;14(2):474-493. doi: 10.21037/jtd-22-126. J Thorac Dis. 2022. PMID: 35280469 Free PMC article.
-
A New Strategy for Deleting Animal drugs from Traditional Chinese Medicines based on Modified Yimusake Formula.Sci Rep. 2017 May 4;7(1):1504. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-01613-7. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28473709 Free PMC article.
-
In silico-based screen synergistic drug combinations from herb medicines: a case using Cistanche tubulosa.Sci Rep. 2017 Nov 27;7(1):16364. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-16571-3. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 29180652 Free PMC article.
-
Dengue virus causes changes of MicroRNA-genes regulatory network revealing potential targets for antiviral drugs.BMC Syst Biol. 2018 Jan 4;12(1):2. doi: 10.1186/s12918-017-0518-x. BMC Syst Biol. 2018. PMID: 29301573 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic Potential of Genipin in Central Neurodegenerative Diseases.CNS Drugs. 2016 Oct;30(10):889-97. doi: 10.1007/s40263-016-0369-9. CNS Drugs. 2016. PMID: 27395402 Review.
References
-
- Normile D (2003) Asian medicine. The new face of traditional Chinese medicine. Science 299: 188–190. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

