Involvement of the caleosin/peroxygenase RD20 in the control of cell death during Arabidopsis responses to pathogens
- PMID: 25830533
- PMCID: PMC4622875
- DOI: 10.4161/15592324.2014.991574
Involvement of the caleosin/peroxygenase RD20 in the control of cell death during Arabidopsis responses to pathogens
Abstract
Caleosins, mostly found in lipid droplets of seeds and leaves, are believed to play physiological roles through their enzymatic capacities to produce oxylipins. We recently identified the caleosin RD20 as a peroxygenase reducing endogenous fatty acid hydroperoxides into their corresponding alcohols. Such oxylipins confer tolerance to oxidative stress by decreasing reactive oxygen species accumulation and by minimizing cell death. RD20 expression being induced by pathogens, we have examined the mode of action of this caleosin in response to biotic stress. Plants overexpressing RD20 exhibited an alteration of their leaf cuticle wax components and an increased resistance to the fungus Alternaria brassicicola. Conversely, silencing RD20 led to an enhanced propagation of the fungus and to reduced severity of the damages caused by the inoculation of the bacteria Pseudomonas syringae pv tomato. We discuss these findings and propose that the major function of RD20 is to generate oxylipins modulating oxidative status and cell death.
Keywords: Alternaria; Pseudomonas; RD20; caleosin; cell death; defense; oxylipins; reactive oxygen species.
Figures

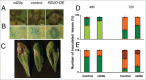
 Stage I,
Stage I,  Stage II,
Stage II,  Stage III,
Stage III,  Stage IV. The damages were significantly different from those of the control when **P < 0.05 (t-test).
Stage IV. The damages were significantly different from those of the control when **P < 0.05 (t-test).References
-
- Prost I, Dhondt S, Rothe G, Vicente J, Rodriguez MJ, Kift N, Carbonne F, Griffiths G, Esquerré-Tugayé MT, Rosahl S, et al. . Evaluation of the antimicrobial activities of plant oxylipins support their involvement in defense against pathogens. Plant Physiol 2005; 139:1902-13; PMID:16299186; http://dx.doi.org/10.1104/pp.105.066274 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lòpez MA, Vicente J, Kulaserakan S, Vellosillo T, Martinez M, Irigoyen MI, Cascòn T, Bannenberg G, Hamberg M, Castresana C. Antagonistic role of 9-lipoxygenase-derived oxylipins and ethylene in the control of oxidative stress, lipid peroxidation and plant defence. Plant J 2011; 67:447-58; PMID:21481031; http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2011.04608.x - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ponce de Leòn I, Sanz A, Hamberg M, Castresana C. Involvement of α-DOX1 fatty acid dioxygenase in protection against oxidative stress and cell death. Plant J 2002; 29:61-72; PMID:12060227; http://dx.doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-313x.2002.01195.x - DOI - PubMed
-
- Mosblech A, Feussner I, Heilmann I. Oxylipins: structurally diverse metabolites from fatty acid oxidation. Plant Physiol Biochem 2009; 47:511-17; PMID:19167233; http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2008.12.011 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hamberg M, Sanz A, Castresana C. Alpha-oxidation of fatty acids in higher plants: identification of a pathogen-inducible oxygenase (piox) as an alpha-dioxygenase and biosynthesis of 2-hydroperoxylinolenic acid. J Biol Chem 1999; 274: 24503-13; PMID:10455113; http://dx.doi.org/10.1074/jbc.274.35.24503 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
