Blood lead levels in children aged 0-6 years old in Hunan Province, China from 2009-2013
- PMID: 25830596
- PMCID: PMC4382167
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0122710
Blood lead levels in children aged 0-6 years old in Hunan Province, China from 2009-2013
Abstract
Objectives: The aim of this study is to describe blood lead levels (BLLs) and the prevalence of elevated blood lead levels (EBLLs) in children aged 0-6 years old and to analyze the BLL trend in children from 2009 to 2013 in China.
Methods: A total of 124,376 children aged 0-6 years old were recruited for this study from January 1st 2009 to December 31st 2013. Their blood lead levels were analyzed using atomic absorption spectrometry.
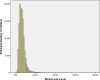
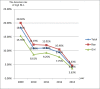
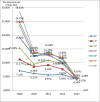
Results: The median BLL was 64.3 μg/L (IQR: 49.6-81.0), and the range was 4.3-799.0 μg/L. Blood lead levels were significantly higher in boys (66.0 μg/L) than in girls (61.9 μg/L) (P<0.001). The overall prevalence of BLLs≥100 μg/L was 10.54% in children aged 0-6 years in Hunan Province. Between 2009 and 2013, the prevalence of EBLLs (≥100 μg/L) decreased from 18.31% to 4.26% in children aged 0-6 years and increased with age. The prevalence of EBLLs has dramatically decreased in two stages (2009-2010 and 2012-2013), with a slight fluctuation in 2010 and 2011.
Conclusions: Both BLLs and the prevalence of EBLLs in children aged 0-6 years old declined substantially from 2009 to 2013 in Hunan Province; however, both remain at unacceptably high levels compared to developed countries. Comprehensive strategies are required to further reduce blood lead levels in children.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Rogan WJ, Ware JH. Intellectual impairment in children with blood lead concentrations below 10 microg per deciliter. J Pediatr. 2003;143(5):687–8. - PubMed
-
- Glenn BS, Bandeen-Roche K, Lee BK, Weaver VM, Todd AC, Schwartz BS. Changes in systolic blood pressure associated with lead in blood and bone. Epidemiology. 2006;17(5):538–44. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical