Low molecular weight chitosan-insulin polyelectrolyte complex: characterization and stability studies
- PMID: 25830681
- PMCID: PMC4413186
- DOI: 10.3390/md13041765
Low molecular weight chitosan-insulin polyelectrolyte complex: characterization and stability studies
Abstract
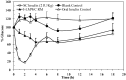
The aim of the work reported herein was to investigate the effect of various low molecular weight chitosans (LMWCs) on the stability of insulin using USP HPLC methods. Insulin was found to be stable in a polyelectrolyte complex (PEC) consisting of insulin and LMWC in the presence of a Tris-buffer at pH 6.5. In the presence of LMWC, the stability of insulin increased with decreasing molecular weight of LMWC; 13 kDa LMWC was the most efficient molecular weight for enhancing the physical and chemical stability of insulin. Solubilization of insulin-LMWC polyelectrolyte complex (I-LMWC PEC) in a reverse micelle (RM) system, administered to diabetic rats, results in an oral delivery system for insulin with acceptable bioactivity.
Figures


References
-
- Hiroyuki H., Tsutomu A., Kentaro S. Effect of additives on protein aggregation. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2009;19:400–407. - PubMed
-
- Aranaz I., Harris R., Heras A. Chitosan amphiphilic derivatives chemistry and applications. Curr. Org. Chem. 2010;14:308–330. doi: 10.2174/138527210790231919. - DOI
-
- Junginger H.E. Polymeric permeation enhancers. In: Bernkop-Schnürch A., editor. Oral Delivery of Macromolecular Drugs. Springer Dordrecht Heidelberg; New York, NY, USA: 2009. pp. 103–136.
-
- Sadeghi A.M., Dorkoosh F.A., Avadi M.R., Saadat P., Rafiee-Tehrani M., Junginger H.E. Preparation, characterization and antibacterial activities of chitosan, N-trimethyl chitosan (TMC) and N-diethylmethyl chitosan (DEMC) nanoparticles loaded with insulin using both the ionotropic gelation and polyelectrolyte complexation methods. Int. J. Pharm. 2008;355:299–306. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2007.11.052. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

