Auranofin exerts broad-spectrum bactericidal activities by targeting thiol-redox homeostasis
- PMID: 25831516
- PMCID: PMC4394260
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1504022112
Auranofin exerts broad-spectrum bactericidal activities by targeting thiol-redox homeostasis
Abstract
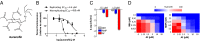
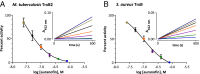
Infections caused by antibiotic-resistant bacteria are a rising public health threat and make the identification of new antibiotics a priority. From a cell-based screen for bactericidal compounds against Mycobacterium tuberculosis under nutrient-deprivation conditions we identified auranofin, an orally bioavailable FDA-approved antirheumatic drug, as having potent bactericidal activities against both replicating and nonreplicating M. tuberculosis. We also found that auranofin is active against other Gram-positive bacteria, including Bacillus subtilis and Enterococcus faecalis, and drug-sensitive and drug-resistant strains of Enterococcus faecium and Staphylococcus aureus. Our biochemical studies showed that auranofin inhibits the bacterial thioredoxin reductase, a protein essential in many Gram-positive bacteria for maintaining the thiol-redox balance and protecting against reactive oxidative species. Auranofin decreases the reducing capacity of target bacteria, thereby sensitizing them to oxidative stress. Finally, auranofin was efficacious in a murine model of methicillin-resistant S. aureus infection. These results suggest that the thioredoxin-mediated redox cascade of Gram-positive pathogens is a valid target for the development of antibacterial drugs, and that the existing clinical agent auranofin may be repurposed to aid in the treatment of several important antibiotic-resistant pathogens.
Keywords: Gram-positive; MRSA; auranofin; tuberculosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Boucher HW, et al. Bad bugs, no drugs: No ESKAPE! An update from the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin Infect Dis. 2009;48(1):1–12. - PubMed
-
- Arias CA, Murray BE. Antibiotic-resistant bugs in the 21st century—a clinical super-challenge. N Engl J Med. 2009;360(5):439–443. - PubMed
-
- Klevens RM, et al. Active Bacterial Core surveillance (ABCs) MRSA Investigators Invasive methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections in the United States. JAMA. 2007;298(15):1763–1771. - PubMed
-
- Abubakar I, et al. Drug-resistant tuberculosis: Time for visionary political leadership. Lancet Infect Dis. 2013;13(6):529–539. - PubMed
-
- Koul A, Arnoult E, Lounis N, Guillemont J, Andries K. The challenge of new drug discovery for tuberculosis. Nature. 2011;469(7331):483–490. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

